Automotive Mechanic Training for English Speakers in France
In France, individuals who speak English and are interested in automotive mechanics can engage in specialized training programs designed to equip them with essential skills. This training is accessible even for those with no prior experience in the field. Engaging in mechanic training provides a pathway to navigate the dynamic automotive industry, offering foundational knowledge and practical skills necessary for a successful career.
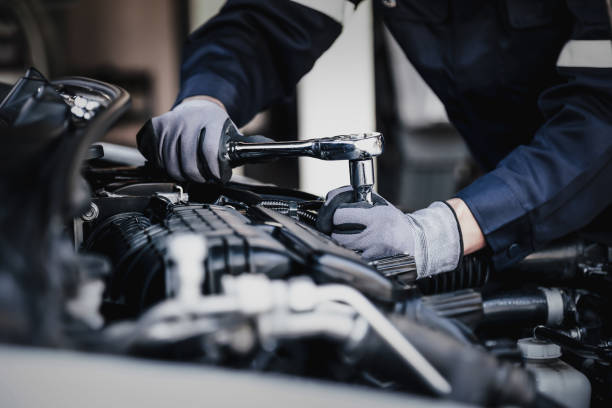

France’s automotive industry represents one of Europe’s most dynamic sectors, creating substantial opportunities for skilled mechanics and technicians. The country hosts major automotive manufacturers and suppliers, generating consistent demand for qualified professionals who can service, maintain, and repair modern vehicles. English-speaking individuals considering automotive mechanic training in France will find a structured educational landscape that accommodates international students while providing comprehensive technical education.
Understanding the Automotive Mechanic Training Landscape in France
French automotive mechanic training operates through multiple educational channels, including technical colleges, vocational institutes, and apprenticeship programs. The French qualification system recognizes several certification levels, from CAP (Certificat d’Aptitude Professionnelle) to BTS (Brevet de Technicien Supérieur), each designed to meet specific industry requirements. Training programs typically combine theoretical instruction with practical workshop experience, ensuring students develop both conceptual understanding and hands-on skills. Many institutions offer specialized tracks focusing on diesel engines, hybrid systems, electronic diagnostics, or specific vehicle brands, allowing students to tailor their education to particular career interests.
Benefits of Pursuing Mechanic Training for English Speakers
English-speaking students pursuing automotive mechanic training in France gain access to European automotive standards and practices, which differ significantly from other international systems. French training programs emphasize precision, quality control, and systematic diagnostic approaches that align with European Union regulations and manufacturer specifications. Students develop familiarity with European vehicle models, parts sourcing, and repair methodologies that enhance their professional versatility. Additionally, completing training in France provides pathways to employment throughout the European Union, as French automotive qualifications are widely recognized across member countries. Language immersion during training also develops valuable multilingual communication skills that prove advantageous in international automotive careers.
The Pathway to Becoming a Skilled Automotive Mechanic
Becoming a qualified automotive mechanic in France requires following established educational and certification pathways. Initial training typically begins with foundational courses covering basic mechanical principles, engine operation, electrical systems, and safety protocols. Students progress through increasingly specialized modules addressing advanced diagnostics, computer-controlled systems, and emerging technologies like electric and hybrid powertrains. Practical training occurs in well-equipped workshops featuring current diagnostic equipment, vehicle lifts, and specialized tools that mirror professional garage environments. Many programs incorporate internships or apprenticeships with local automotive businesses, providing real-world experience while building professional networks.
| Training Program | Institution Type | Duration | Estimated Cost Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| CAP Maintenance Véhicules | Public Vocational School | 2 years | Low to moderate tuition |
| BTS Après-Vente Automobile | Technical College | 2 years | Moderate annual fees |
| Professional Apprenticeship | Employer Partnership | 1-3 years | Paid training with wages |
| Private Training Centers | Commercial Institutions | 6-18 months | Higher investment required |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on general market information and may vary significantly depending on specific institutions, program content, and individual circumstances. Costs can change over time due to policy updates, funding changes, or institutional decisions. Independent research and direct contact with training providers is strongly advised before making financial commitments.
Successful completion of automotive mechanic training in France opens diverse career opportunities across the automotive sector. Graduates may pursue employment in independent repair shops, authorized dealerships, fleet maintenance operations, or specialized service centers. The French automotive market includes both traditional internal combustion vehicles and increasing numbers of electric and hybrid models, creating demand for technicians skilled in emerging technologies. Career advancement opportunities include supervisory roles, specialized diagnostic positions, or entrepreneurial ventures establishing independent automotive service businesses.
Training programs also address contemporary automotive challenges, including environmental regulations, emission control systems, and sustainable repair practices. Students learn about proper waste disposal, recycling protocols, and energy-efficient repair techniques that align with French environmental standards. This comprehensive approach ensures graduates understand both technical and regulatory aspects of modern automotive service.
Automotive mechanic training for English speakers in France provides a solid foundation for rewarding careers in a dynamic industry. The combination of rigorous technical education, practical experience, and exposure to European automotive standards creates well-rounded professionals capable of meeting contemporary automotive service demands. With proper planning and commitment, English-speaking students can successfully navigate French training systems and establish successful careers in the automotive sector.