Aviation Training Programs for English Speakers in the UK
Individuals residing in the United Kingdom and proficient in English may consider training in aviation to pursue roles at airports. Aviation training programs provide foundational knowledge and skills necessary for various positions within the airport environment, covering topics such as regulations, safety protocols, and operational procedures. Engaging in these programs can lead to a deeper understanding of the aviation industry and its operational dynamics.
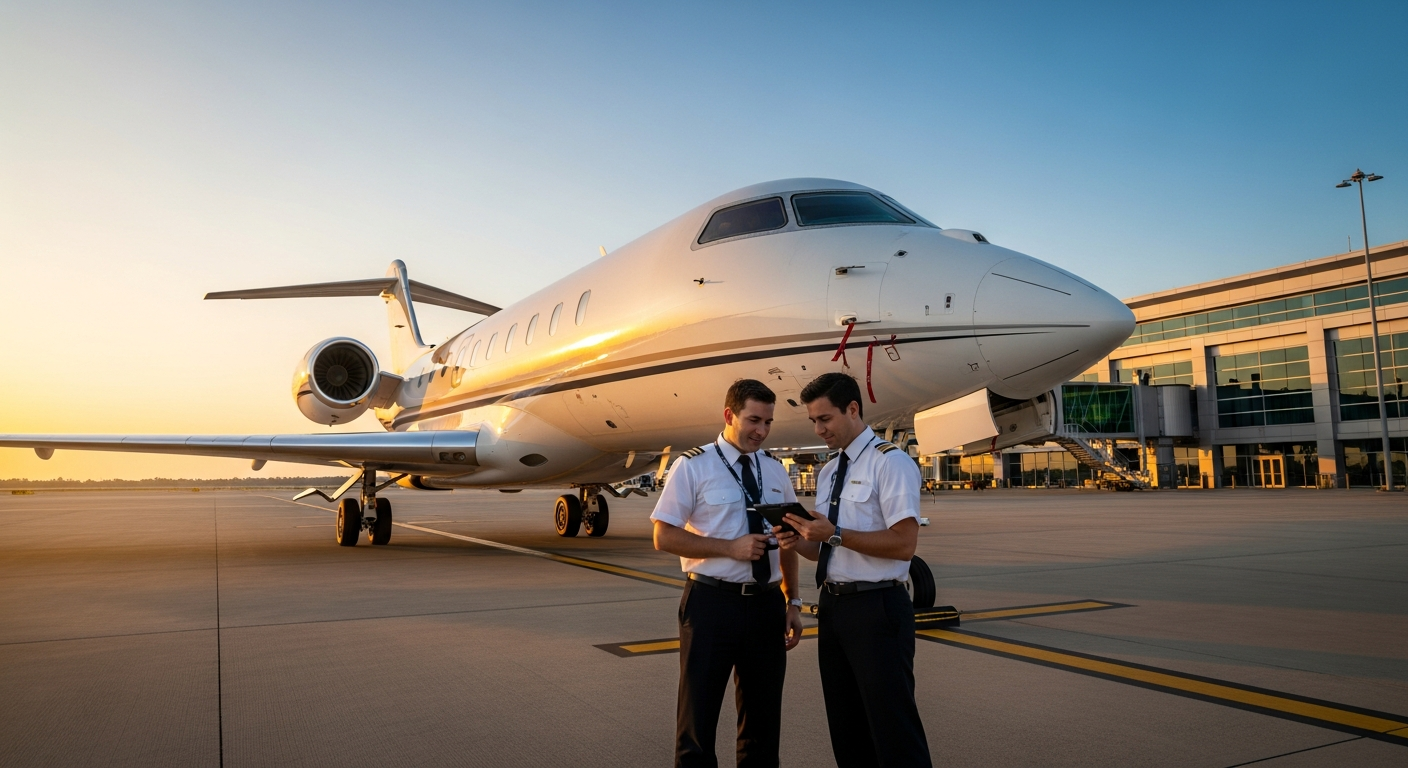

Aviation training in the United Kingdom represents one of the most structured and comprehensive approaches to preparing future aviation professionals. The country’s rich aviation heritage, combined with modern training methodologies, creates an environment where students can develop the skills necessary for various aviation careers.
Understanding the Basics of Aviation Training Programs in the UK
Aviation training programs in the UK are designed around internationally recognised standards set by the Civil Aviation Authority (CAA) and European Union Aviation Safety Agency (EASA). These programs typically begin with ground school instruction covering aerodynamics, navigation, meteorology, aircraft systems, and aviation law. Students learn fundamental principles through classroom lectures, computer-based training modules, and interactive simulations.
Flight training follows a progressive structure, starting with basic aircraft handling and advancing to complex manoeuvres and emergency procedures. Training aircraft range from single-engine Cessna 152s for initial instruction to multi-engine commercial aircraft for advanced certification. Most programs integrate both visual flight rules (VFR) and instrument flight rules (IFR) training, ensuring graduates can operate in various weather conditions and airspace environments.
Requirements for Participating in Aviation Training Programs
Prospective aviation students must meet specific medical, educational, and legal requirements before beginning training. Medical certification requires passing a Class 1 medical examination conducted by an authorised aviation medical examiner, ensuring candidates have the physical and mental capabilities necessary for safe flight operations. Vision, hearing, cardiovascular health, and psychological fitness are thoroughly evaluated.
Educational prerequisites vary depending on the specific program and career path. Commercial pilot training typically requires a minimum of five GCSEs or equivalent qualifications, including mathematics and English. Some integrated programs prefer A-levels or university degrees, particularly for airline transport pilot licence pathways. Age requirements specify minimum ages of 17 for private pilot licences and 21 for commercial pilot licences.
Language proficiency represents another crucial requirement, with English language skills assessed according to International Civil Aviation Organization standards. Candidates must demonstrate proficiency in aviation English, including technical terminology and radio communication procedures.
Potential Career Paths After Completing Aviation Training
Completed aviation training opens numerous career opportunities across different sectors of the industry. Commercial airline pilots represent the most visible career path, with opportunities ranging from regional carriers to major international airlines. These positions offer structured career progression from first officer to captain, with potential advancement to training captain or management roles.
Corporate and business aviation provides alternative career paths for pilots seeking variety and personalised service environments. Charter operations, executive transport, and specialised missions like medical evacuation or cargo transport offer diverse flying experiences. Many pilots find satisfaction in flight instruction, sharing their expertise with the next generation of aviators while building flight hours and experience.
Aviation careers extend beyond piloting to include air traffic control, aircraft maintenance, aviation management, and airport operations. Flight dispatchers coordinate flight planning and operational decisions, while aviation safety inspectors ensure regulatory compliance across the industry.
| Training Provider | Program Type | Duration | Cost Estimation |
|---|---|---|---|
| CAE Oxford | Integrated ATPL | 18-24 months | £80,000-£120,000 |
| Bristol Groundschool | Modular Training | 12-18 months | £60,000-£90,000 |
| FTA Global | Commercial Pilot | 14-20 months | £70,000-£100,000 |
| Cranfield University | MSc Air Transport | 12 months | £25,000-£35,000 |
| Cabair College | PPL to CPL | 8-12 months | £45,000-£65,000 |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
The financial investment in aviation training reflects the comprehensive nature of these programs and the sophisticated equipment required. Training costs include aircraft rental, fuel, instructor fees, examination fees, and equipment purchases. Many students explore financing options, including career development loans, airline sponsorship programs, and payment plans offered by training organisations.
Successful completion of aviation training programs results in internationally recognised licences and ratings that enable graduates to pursue careers worldwide. The skills developed through rigorous training, including decision-making under pressure, technical proficiency, and safety consciousness, prove valuable throughout aviation careers and often transfer to other professional environments.
Aviation training in the UK continues evolving with technological advances and industry requirements. Modern programs incorporate advanced flight simulators, computer-based training systems, and emerging technologies like virtual reality instruction. These innovations enhance learning effectiveness while maintaining the high safety standards that characterise British aviation training.