Explore Exciting Security Job Opportunities Across Germany
For individuals in Germany seeking to embark on a career as a security guard, various entry-level opportunities are available. This exploration of security roles offers insights into job responsibilities, necessary skills, and pathways to secure positions within the industry. Understanding these elements can greatly assist those interested in beginning their professional journey in security.
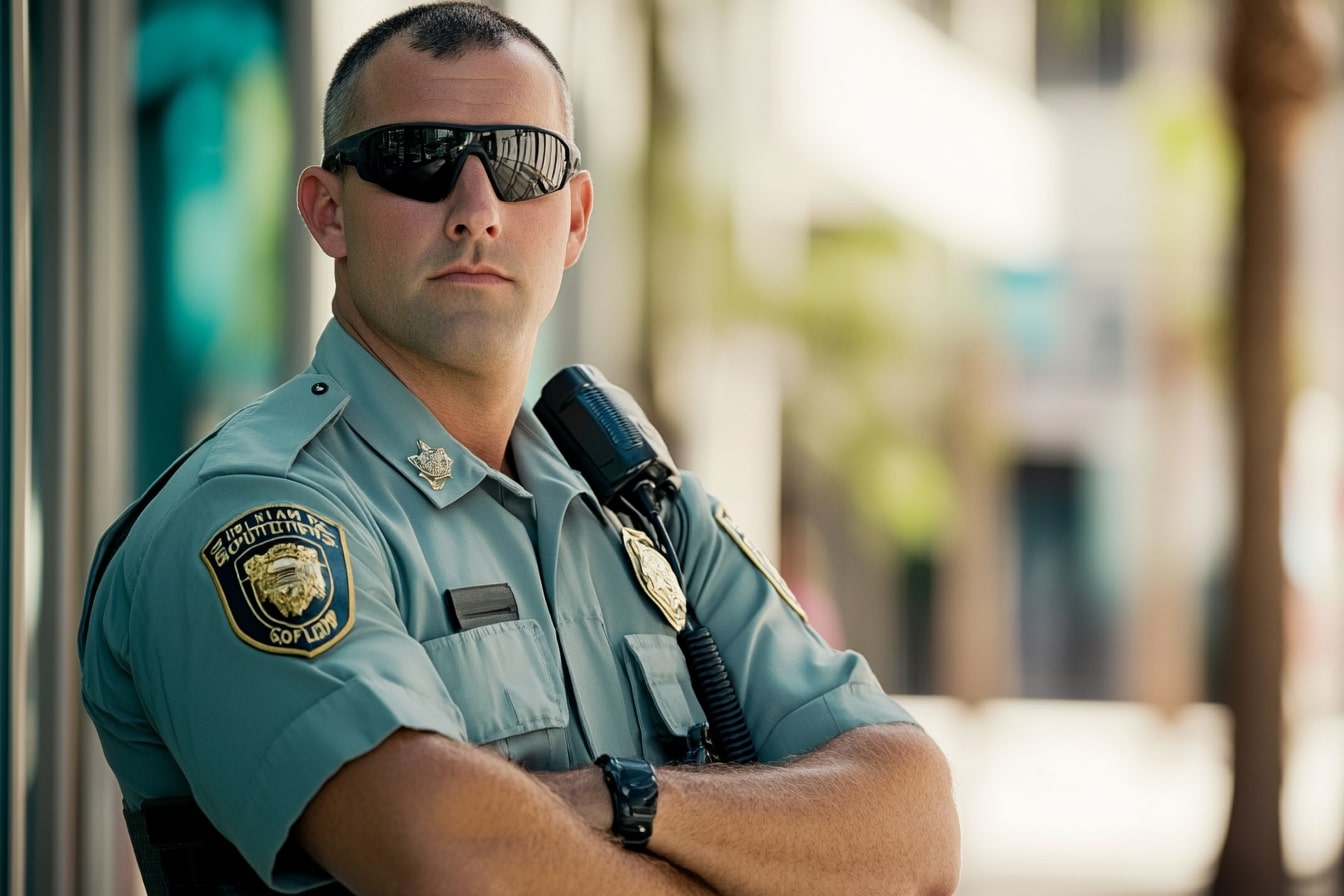

Understanding the Role of a Security Guard in Germany
Security guards in Germany fulfill multiple essential functions beyond the common perception of simply monitoring entrances. Their responsibilities typically include conducting regular patrols of assigned areas, monitoring surveillance systems, controlling access points, checking visitor credentials, and maintaining detailed incident reports. In Germany, security personnel operate under specific regulatory frameworks that require thorough documentation and adherence to standardized procedures.
The German security industry differentiates between various roles, including object protection (Objektschutz), personal security (Personenschutz), event security (Veranstaltungssicherheit), and retail security (Einzelhandelssicherheit). Each specialization requires different skill sets and training, with object protection focusing on property surveillance, while personal security demands heightened situational awareness and conflict management abilities.
Many security professionals in Germany also serve as first responders during emergencies, performing preliminary first aid and coordinating with emergency services until specialized help arrives. This aspect of the job requires composure under pressure and the ability to make quick, rational decisions in stressful situations.
Essential Skills Required for a Successful Security Career
Success in the German security sector depends on developing a combination of hard and soft skills that enable professionals to handle diverse situations effectively. Communication skills rank among the most important attributes, as security personnel must interact clearly with colleagues, supervisors, the public, and sometimes law enforcement. This includes proficiency in German, with English often considered a valuable additional skill, particularly in international settings.
Physical fitness and mental alertness are fundamental requirements, as security work often involves long periods of standing, walking, and maintaining vigilance. Observation skills and attention to detail allow security professionals to detect unusual activities or potential threats before they escalate into serious incidents.
Technical competencies are increasingly important in the modernizing security landscape. Familiarity with electronic surveillance systems, access control software, alarm systems, and communication equipment provides security professionals with a competitive advantage in the job market. Many employers also value computer literacy for documentation and reporting purposes.
Interpersonal skills and emotional intelligence significantly impact effectiveness in security roles. De-escalation techniques and conflict resolution abilities are particularly valuable, as security personnel frequently encounter tense situations that require calm management rather than force. Critical thinking and problem-solving capabilities enable quick assessment and response to unexpected developments.
Pathways to Begin Your Journey in the Security Industry
Entering the security profession in Germany typically begins with obtaining the mandatory Security Certificate (Bewachungsgewerbe Paragraph 34a), often referred to as the “34a Certificate.” This certification involves completing an 80-hour training course covering legal foundations, emergency response, conflict management, and security practices, followed by an examination administered by the local Chamber of Industry and Commerce (IHK).
For those seeking advanced positions, additional qualifications can significantly enhance career prospects. The IHK offers specialized certifications for roles such as security specialist (Geprüfter Schutz- und Sicherheitskraft) and security manager (Meister für Schutz und Sicherheit), which require further training and professional experience.
Prior experience in related fields often proves beneficial when transitioning to security work. Former police officers, military personnel, firefighters, and individuals with backgrounds in customer service frequently find their skills transferable to security positions. These backgrounds provide valuable perspectives on safety protocols, emergency response, and public interaction.
Networking plays a significant role in securing employment within the industry. Professional associations like the German Association for Security in the Economy (ASW) and the Federal Association of German Security Companies (BDSW) offer opportunities to connect with potential employers and stay informed about developments in the field.
Security Job Market and Employment Conditions in Germany
The security sector in Germany has experienced consistent growth over recent years, driven by increased awareness of security concerns across public and private sectors. Major urban centers like Berlin, Hamburg, Munich, and Frankfurt offer the highest concentration of opportunities, though security services are required throughout the country.
Employment conditions vary considerably depending on the employer, position level, and specialization. Entry-level positions typically offer hourly wages ranging from €10-15, with night shifts, weekends, and holidays often commanding premium rates. With additional qualifications and experience, security professionals can progress to supervisory and management roles with corresponding salary increases.
Contract structures in the German security industry include both part-time and full-time positions, with shift work common across most roles. Some employers offer additional benefits such as transportation allowances, meal subsidies, and comprehensive training programs. The collective bargaining agreement for security services (Tarifvertrag für Sicherheitsdienstleistungen) establishes minimum standards for wages and working conditions in many employment relationships.
The COVID-19 pandemic has created additional demand for security personnel in certain sectors, particularly for enforcing health and safety protocols at retail establishments, testing centers, and vaccination facilities. This trend has opened new specialization opportunities within the industry.
Emerging Trends and Future Prospects in German Security
The security industry in Germany continues to evolve with technological advancements and changing security needs. Integrated security solutions combining human personnel with electronic systems represent one of the fastest-growing segments of the market, creating demand for security professionals with technical expertise alongside traditional skills.
Cybersecurity integration is becoming increasingly relevant, even for physical security roles, as systems become more interconnected. Security professionals who understand both physical and digital vulnerabilities position themselves advantageously in this evolving landscape.
Specialized security services tailored to specific industries—healthcare, logistics, manufacturing, and critical infrastructure protection—present opportunities for career differentiation. These sectors often offer more favorable compensation and working conditions than general security services due to the specialized knowledge required.
For those interested in long-term career development, the German security industry offers pathways to entrepreneurship through establishing independent security consulting firms or specialized service providers. The structured certification system provides a clear framework for professional advancement that can eventually lead to business ownership.
With Germany’s continued focus on public safety and private security, the sector remains a stable career choice with opportunities for growth, specialization, and professional development across the country.