Food Industry in Higashiosaka – General Overview
In Higashiosaka, the food industry is commonly described as a highly organized sector within the broader urban economy. It includes structured processes related to food preparation, handling, packaging, and distribution, supported by quality standards and regulated workflows. This overview provides general information on how working conditions and operational structures in the food sector are typically presented.
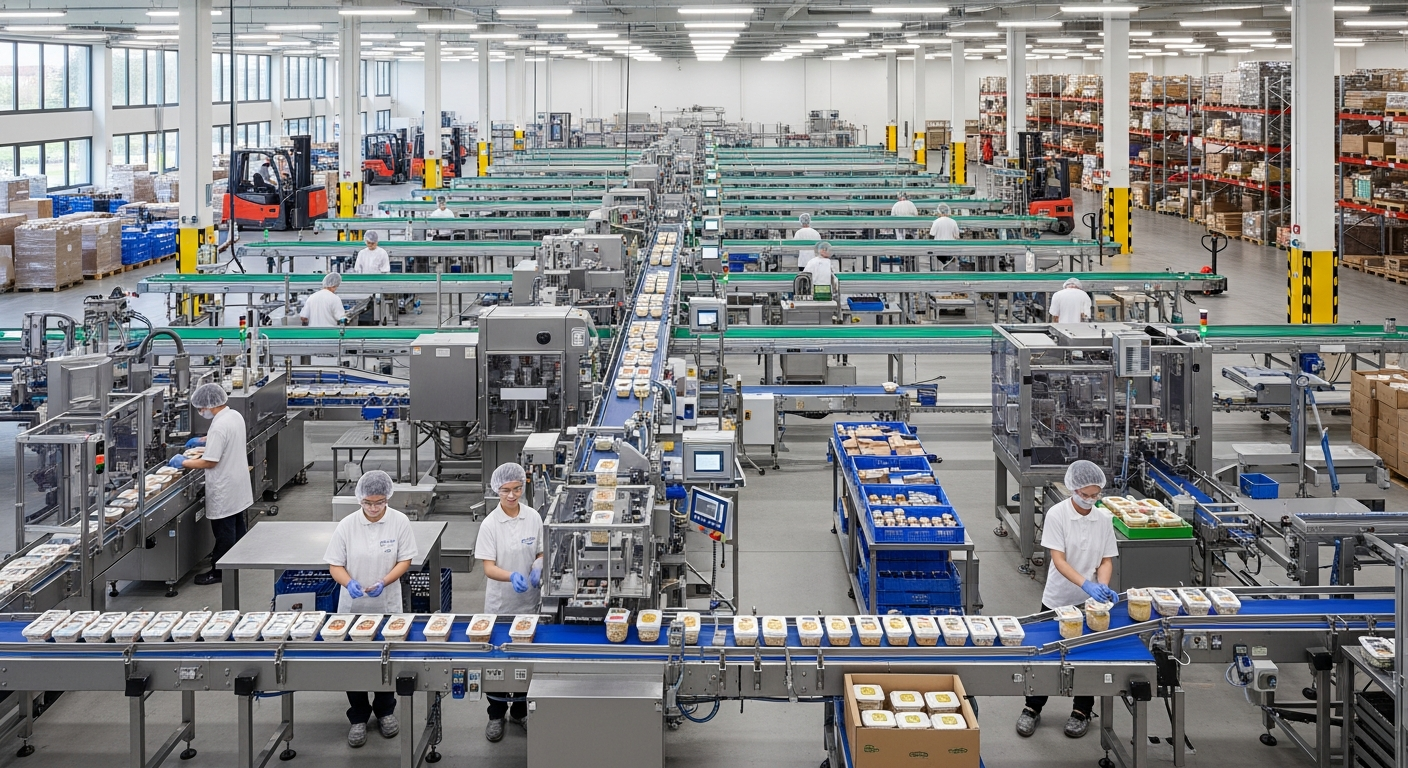

The food industry in Higashiosaka represents a cornerstone of the city’s manufacturing sector, contributing significantly to both local employment and regional economic stability. Located strategically within the greater Osaka metropolitan area, this industrial city has developed into a hub for various food-related operations, from primary processing to final packaging and distribution.
What Defines the Food Industry Higashiosaka Landscape
The food industry landscape in Higashiosaka is characterized by its diversity and integration within the broader manufacturing ecosystem. The city hosts approximately 200 food-related businesses, ranging from traditional confectionery makers to modern beverage bottling facilities. These operations benefit from the city’s excellent transportation infrastructure, including proximity to Osaka Bay for import/export activities and extensive rail networks connecting to major population centers.
The sector encompasses multiple categories including processed foods, beverages, confectionery products, and ready-to-eat meals. Many facilities focus on contract manufacturing, producing goods for major Japanese food brands while maintaining strict quality standards required by the domestic market. The presence of supporting industries, such as packaging material manufacturers and food machinery suppliers, creates a comprehensive industrial cluster.
Understanding the Urban Food Sector Structure
The urban food sector structure in Higashiosaka reflects Japan’s broader industrial organization patterns. Small and medium-sized enterprises form the backbone of the industry, with many companies employing between 20 to 100 workers. These businesses often specialize in specific product categories or manufacturing processes, allowing them to develop expertise and maintain competitive advantages.
Large multinational corporations also maintain significant operations in the area, particularly in beverage production and snack food manufacturing. These facilities typically employ advanced automation systems and maintain higher production volumes compared to smaller operations. The coexistence of different company sizes creates a dynamic environment where innovation and traditional craftsmanship complement each other.
Supply chain integration plays a crucial role in the sector’s structure. Many companies maintain long-term relationships with suppliers and distributors, creating stable business networks that support consistent production schedules and quality maintenance.
How Structured Production Processes Function
Structured production processes in Higashiosaka’s food industry follow rigorous standards established by Japanese food safety regulations and international quality certifications. Most facilities operate under HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points) systems, ensuring systematic approaches to food safety throughout the production cycle.
Production workflows typically begin with raw material inspection and storage, followed by processing stages that vary depending on the product type. Automated systems handle much of the packaging and labeling processes, while quality control checkpoints occur at multiple stages throughout production. Many facilities operate on continuous production schedules to maximize efficiency and meet delivery commitments.
Technology integration has transformed traditional production methods, with computerized monitoring systems tracking everything from ingredient temperatures to packaging seal integrity. However, many companies still maintain manual quality inspection processes, reflecting the Japanese emphasis on attention to detail and product perfection.
| Company Type | Production Focus | Typical Workforce Size |
|---|---|---|
| Small Enterprises | Specialty Products | 10-30 employees |
| Medium Companies | Contract Manufacturing | 50-150 employees |
| Large Corporations | Mass Production | 200-500 employees |
| Beverage Facilities | Bottling Operations | 100-300 employees |
The integration of traditional Japanese manufacturing principles with modern industrial practices creates unique operational characteristics in Higashiosaka’s food sector. Companies emphasize continuous improvement methodologies, employee training programs, and waste reduction initiatives that align with both economic and environmental objectives.
Environmental considerations increasingly influence production processes, with many facilities implementing energy-efficient equipment and waste recycling programs. Water usage optimization and packaging material reduction represent key focus areas for sustainability initiatives across the industry.
The food industry in Higashiosaka continues evolving to meet changing consumer preferences and market demands. Facilities adapt their production capabilities to accommodate smaller batch sizes, customized products, and shorter delivery timeframes while maintaining the quality standards that define Japanese food manufacturing excellence.