Food Industry in Sapporo – General Overview
In Sapporo, the food industry is commonly described as a highly organized sector within the broader urban economy. It includes structured processes related to food preparation, handling, packaging, and distribution, supported by quality standards and regulated workflows. This overview provides general information on how working conditions and operational structures in the food sector are typically presented.

What Defines the Food Industry Sapporo Landscape
Sapporo’s food industry landscape is characterized by its unique blend of traditional Japanese food processing methods and modern industrial techniques. The city serves as a major hub for dairy production, brewing, confectionery manufacturing, and seafood processing. Key factors that define this landscape include the region’s agricultural advantages, with Hokkaido providing high-quality raw materials such as wheat, dairy products, and fresh seafood from nearby coastal areas.
The presence of major food corporations has established Sapporo as a center for innovation in food technology and product development. Companies ranging from large-scale breweries to specialized confectionery manufacturers contribute to a diverse industrial ecosystem. The city’s food industry also benefits from strong research and development capabilities, with several universities and research institutions focusing on food science and agricultural technology.
Understanding the Urban Food Sector Structure
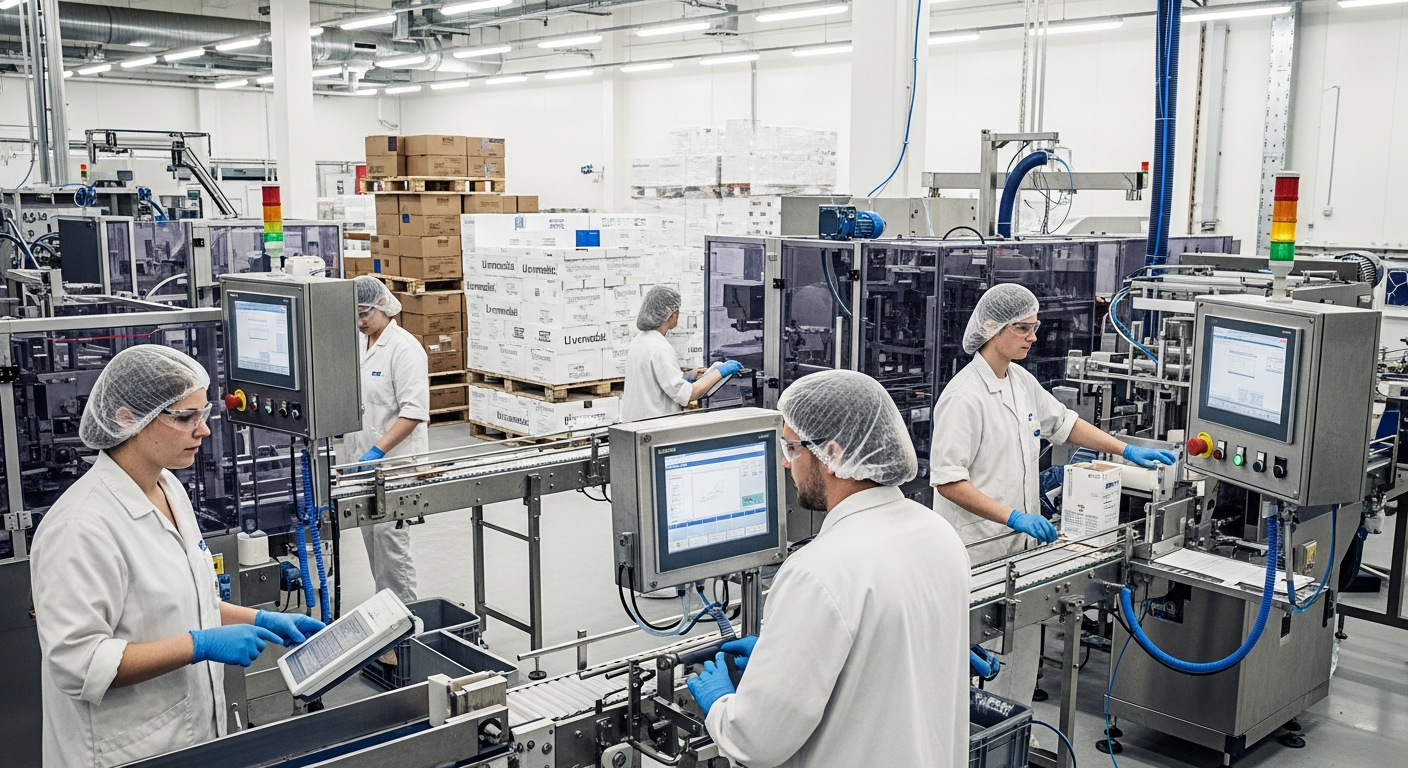
The urban food sector in Sapporo operates through a well-organized network of manufacturing facilities, distribution centers, and processing plants strategically located throughout the metropolitan area. Industrial zones dedicated to food production are typically situated near transportation hubs, facilitating efficient logistics and supply chain management.
Manufacturing facilities range from large-scale operations producing beverages and processed foods to smaller specialized producers focusing on traditional Japanese foods and regional specialties. The sector structure includes primary processing facilities that handle raw agricultural products, secondary processing plants that create finished consumer goods, and packaging and distribution centers that prepare products for market delivery.
Supporting infrastructure includes cold storage facilities, quality control laboratories, and specialized transportation networks designed to maintain food safety standards throughout the production and distribution process.
How Structured Production Processes Function
Production processes in Sapporo’s food industry follow strict protocols designed to ensure quality, safety, and efficiency. These processes typically begin with raw material inspection and preparation, followed by various stages of processing, packaging, and quality assurance testing.
Automated systems play a crucial role in many facilities, with computer-controlled equipment managing tasks such as mixing, cooking, cooling, and packaging. Quality control measures are integrated throughout each stage of production, with regular testing and monitoring to ensure compliance with Japanese food safety regulations and international standards.
Workflow organization emphasizes efficiency and safety, with clearly defined roles for different types of workers. Production schedules are carefully coordinated to maximize equipment utilization while maintaining product quality. Many facilities operate on multiple shifts to meet demand while ensuring proper maintenance and cleaning procedures.
| Sector | Key Companies | Primary Products | Employment Scale |
|---|---|---|---|
| Brewing | Sapporo Breweries, Asahi | Beer, Alcoholic Beverages | Large-scale operations |
| Dairy Processing | Meiji, Morinaga | Milk Products, Cheese | Medium to large facilities |
| Confectionery | Royce’, LeTAO | Chocolates, Sweets | Small to medium operations |
| Seafood Processing | Various Local Companies | Processed Seafood | Small to medium facilities |
The integration of technology and traditional methods creates a production environment that values both efficiency and craftsmanship. Many facilities combine automated processes with skilled manual work, particularly in areas requiring precision or quality assessment that benefits from human expertise.
Environmental considerations are increasingly important in production processes, with many companies implementing sustainable practices such as waste reduction, energy efficiency measures, and environmentally friendly packaging solutions. These initiatives reflect both regulatory requirements and corporate responsibility commitments.
Sapporo’s food industry continues to evolve, adapting to changing consumer preferences, technological advances, and market demands. The sector’s structure supports both large-scale industrial production and smaller specialized operations, creating a diverse and resilient food manufacturing ecosystem that contributes significantly to the local economy and Japan’s broader food industry.