Food Packaging Industry in Fukushima – Structure and Workflows
The food packaging industry in Fukushima is typically presented as a process-driven sector within the food supply chain. Activities follow organized steps related to handling, packing, and quality control. This overview explains in general terms how workflows and working conditions in food packaging environments are usually structured.
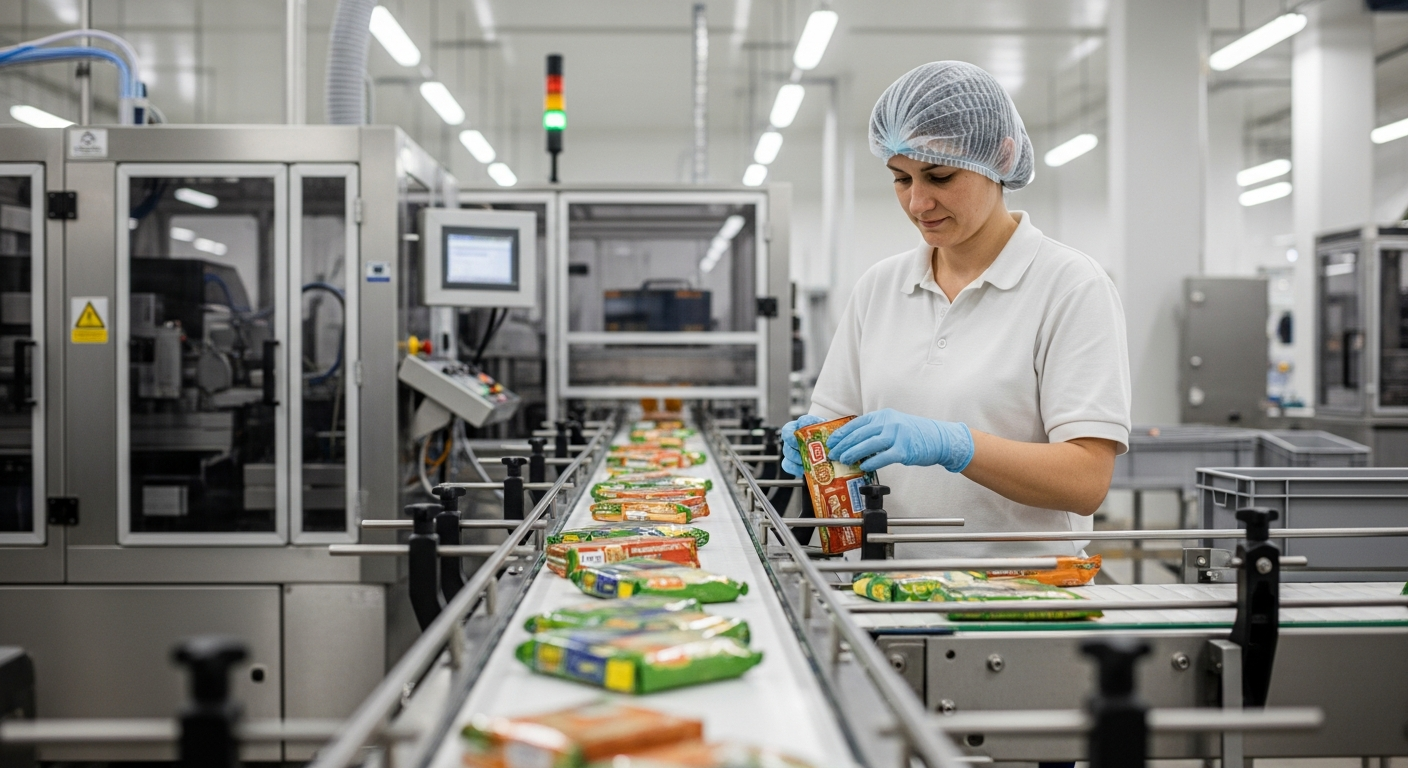

The food packaging sector in Fukushima represents a crucial intersection of manufacturing expertise and agricultural output, serving both domestic and international markets. This industry has evolved considerably, incorporating advanced technologies while maintaining the high standards expected of Japanese manufacturing.
Industry Overview: Current Context
Fukushima’s food packaging industry operates within a complex framework of safety regulations, technological innovation, and market demands. The sector encompasses various packaging types, from traditional materials like paper and cardboard to advanced barrier films and vacuum-sealed containers. Manufacturing facilities in the region typically focus on packaging solutions for rice products, processed foods, and agricultural exports.
The industry structure includes both large-scale manufacturing plants and smaller specialized facilities. These operations employ sophisticated quality management systems that align with Japan’s stringent food safety standards. Production schedules often coordinate closely with seasonal agricultural cycles, particularly during harvest periods when packaging demand peaks.
Workflow optimization has become increasingly important as facilities balance efficiency with precision. Many plants operate multiple shifts to meet varying demand patterns, requiring careful coordination of human resources and machinery maintenance schedules.
Food Packaging in Fukushima: What Makes It Distinct?
Several factors distinguish Fukushima’s food packaging operations from other regions in Japan. The proximity to agricultural production areas creates unique logistical advantages, allowing for shorter supply chains and fresher product handling. This geographic benefit translates into specialized packaging requirements that preserve product quality during distribution.
Local facilities have developed expertise in handling specific product categories, particularly rice and processed agricultural goods. This specialization has led to innovations in packaging materials and techniques that extend shelf life while maintaining product integrity. Many operations have invested in climate-controlled environments and precision sealing equipment.
The region’s manufacturing culture emphasizes continuous improvement, known as kaizen, which influences daily operations. Workers participate in regular process optimization discussions, contributing to efficiency improvements and quality enhancements. This collaborative approach has resulted in packaging solutions that meet both domestic preferences and international export requirements.
Safety protocols receive particular attention, with comprehensive testing procedures and documentation systems. These measures ensure compliance with both national regulations and international standards for food packaging materials.
Production Structure on the Factory Floor
Factory floor operations in Fukushima’s food packaging facilities follow structured workflows designed to maximize efficiency while maintaining quality standards. Production lines typically begin with material preparation areas where packaging components undergo initial quality checks. Raw materials move through designated pathways to prevent contamination and ensure traceability.
Machine operators work in teams, with each member responsible for specific aspects of the packaging process. Line supervisors coordinate between different production stages, monitoring output rates and quality metrics throughout shifts. Regular rotation of responsibilities helps maintain worker engagement and provides cross-training opportunities.
Quality control checkpoints are integrated throughout the production flow, with automated systems detecting defects and manual inspections verifying compliance with specifications. Packaging machines operate according to predetermined parameters, with operators making adjustments based on product requirements and environmental conditions.
Maintenance schedules are carefully planned to minimize production disruptions. Preventive maintenance occurs during scheduled downtime, while emergency repair protocols ensure rapid response to equipment issues. Documentation systems track machine performance, maintenance activities, and production metrics for continuous improvement initiatives.
| Facility Type | Production Focus | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Large-scale Plants | Mass production packaging | Automated lines, high-speed machinery, integrated quality systems |
| Specialized Facilities | Custom packaging solutions | Flexible production lines, specialized materials, small batch capabilities |
| Regional Cooperatives | Agricultural product packaging | Seasonal operations, local product focus, community-based employment |
The integration of technology and human expertise creates a production environment that balances automation with skilled craftsmanship. Workers receive ongoing training in both technical skills and safety procedures, ensuring they can adapt to evolving production requirements and maintain the high standards expected in Japanese manufacturing.
Environmental considerations increasingly influence production decisions, with facilities implementing waste reduction programs and energy-efficient practices. These initiatives align with broader sustainability goals while often resulting in cost savings and improved operational efficiency.
Fukushima’s food packaging industry continues to evolve, incorporating new technologies and responding to changing market demands. The combination of strategic location, skilled workforce, and commitment to quality positions the region as an important contributor to Japan’s food packaging sector, supporting both local economic development and national food security objectives.