Food Packaging Industry in Himeji – Structure and Workflows
The food packaging industry in Himeji is typically presented as a process-driven sector within the food supply chain. Activities follow organized steps related to handling, packing, and quality control. This overview explains in general terms how workflows and working conditions in food packaging environments are usually structured.
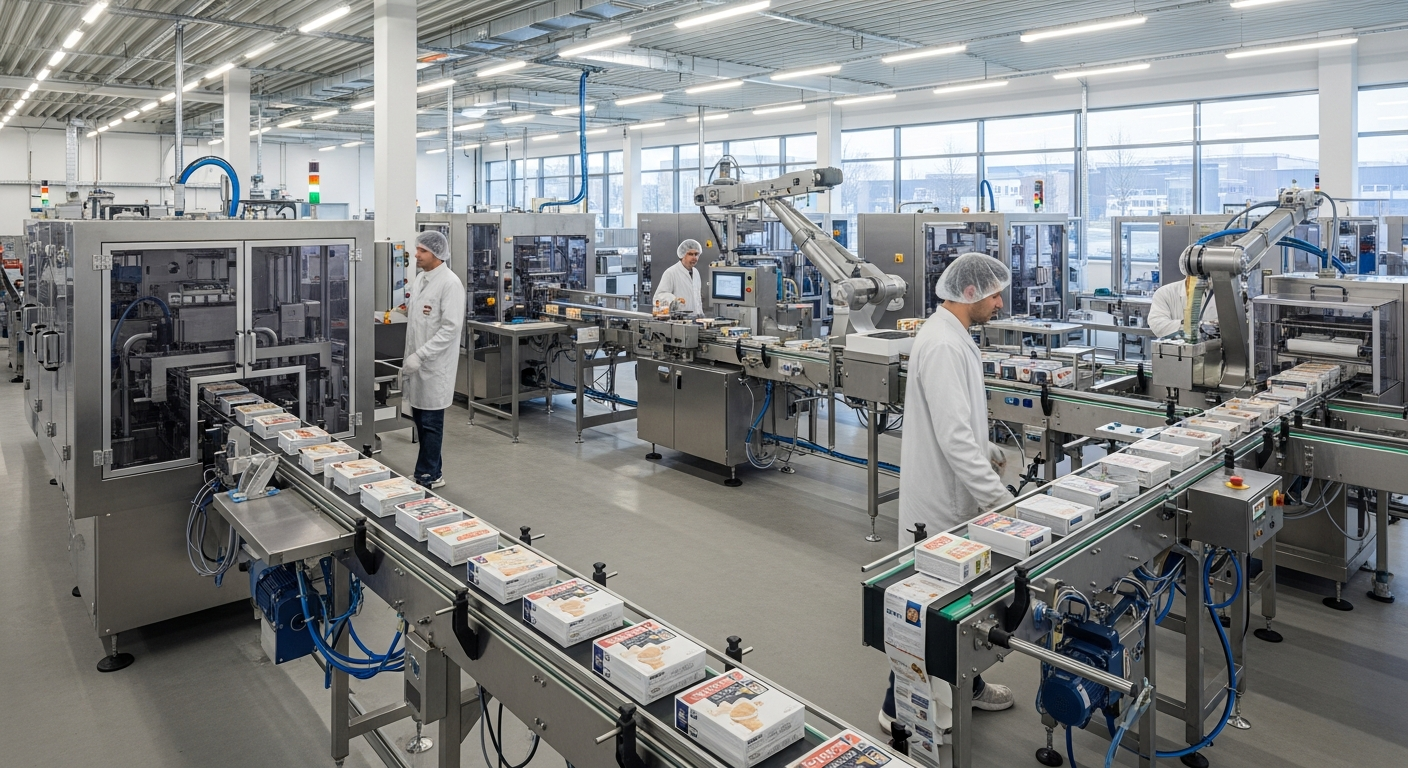

Himeji’s food packaging industry operates within a complex ecosystem that balances efficiency, quality control, and regulatory compliance. The sector encompasses multiple facility types, from large-scale automated plants to specialized packaging centers that handle specific product categories. These operations support both local food manufacturers and major national brands, creating a diverse industrial landscape that adapts to changing market requirements.
Industry Overview: Current Context
The current landscape of food packaging in Himeji reflects broader trends in Japanese manufacturing, emphasizing precision, waste reduction, and technological integration. Facilities typically operate on multi-shift schedules to maximize productivity, with peak periods often coinciding with seasonal food production cycles. The industry has adapted to increased demand for packaged foods, particularly following changes in consumer behavior that prioritize convenience and food safety.
Modern packaging operations incorporate advanced quality assurance systems, including automated inspection technologies and traceability protocols. These systems ensure compliance with Japan’s stringent food safety regulations while maintaining the high standards expected in both domestic and export markets. The integration of digital monitoring systems has become standard practice, allowing for real-time quality control and efficient resource management.
Food Packaging in Himeji: What Makes It Distinct?
Himeji’s geographic position and industrial infrastructure create unique advantages for food packaging operations. The city’s proximity to major transportation networks facilitates efficient distribution to key markets across Japan and internationally. Local facilities benefit from established supply chains that connect regional food producers with packaging specialists, creating integrated production networks.
The region’s approach to food packaging emphasizes flexibility and customization. Many facilities maintain capabilities for handling diverse product types, from traditional Japanese foods requiring specialized preservation methods to international products with specific packaging requirements. This versatility allows operations to adapt to market changes and seasonal variations in food production.
Environmental considerations play an increasingly important role in local packaging operations. Many facilities have implemented sustainable packaging solutions and waste reduction programs that align with Japan’s environmental policies. These initiatives often involve collaboration between packaging companies and food manufacturers to develop eco-friendly alternatives without compromising product quality or safety.
Production Structure on the Factory Floor
The typical production floor in Himeji’s food packaging facilities follows standardized workflows designed for efficiency and quality control. Operations generally begin with incoming material inspection, where packaging materials and products undergo quality verification before entering the production line. This initial stage ensures that only materials meeting specifications proceed to packaging processes.
Production lines are typically organized in linear configurations that minimize handling time and reduce contamination risks. Automated systems handle primary packaging functions, while human operators focus on quality monitoring, equipment maintenance, and specialized tasks requiring manual dexterity. The integration of robotics has increased in recent years, particularly for repetitive tasks such as case packing and palletizing.
Quality control checkpoints are strategically positioned throughout the production flow. These stations utilize various inspection methods, including visual checks, weight verification, and seal integrity testing. Documentation systems track products through each stage, creating comprehensive records that support traceability requirements and facilitate rapid response to any quality issues.
Workflow coordination relies on digital systems that monitor production rates, equipment status, and inventory levels. These systems enable supervisors to optimize line efficiency and coordinate with upstream and downstream operations. Regular maintenance schedules are integrated into production planning to minimize disruptions while ensuring equipment reliability.
The industry continues to evolve with technological advancement and changing market demands. Investment in automation and digital systems reflects the sector’s commitment to maintaining competitiveness while addressing labor market challenges. Training programs ensure that workers develop skills necessary for operating increasingly sophisticated equipment and maintaining quality standards.
Food packaging operations in Himeji demonstrate how traditional manufacturing principles can be enhanced through modern technology and systematic approaches. The industry’s focus on quality, efficiency, and adaptability positions it to meet future challenges while supporting Japan’s food supply chain requirements.