Food Packaging Industry in Hirakata – Structure and Workflows
The food packaging industry in Hirakata is typically presented as a process-driven sector within the food supply chain. Activities follow organized steps related to handling, packing, and quality control. This overview explains in general terms how workflows and working conditions in food packaging environments are usually structured.
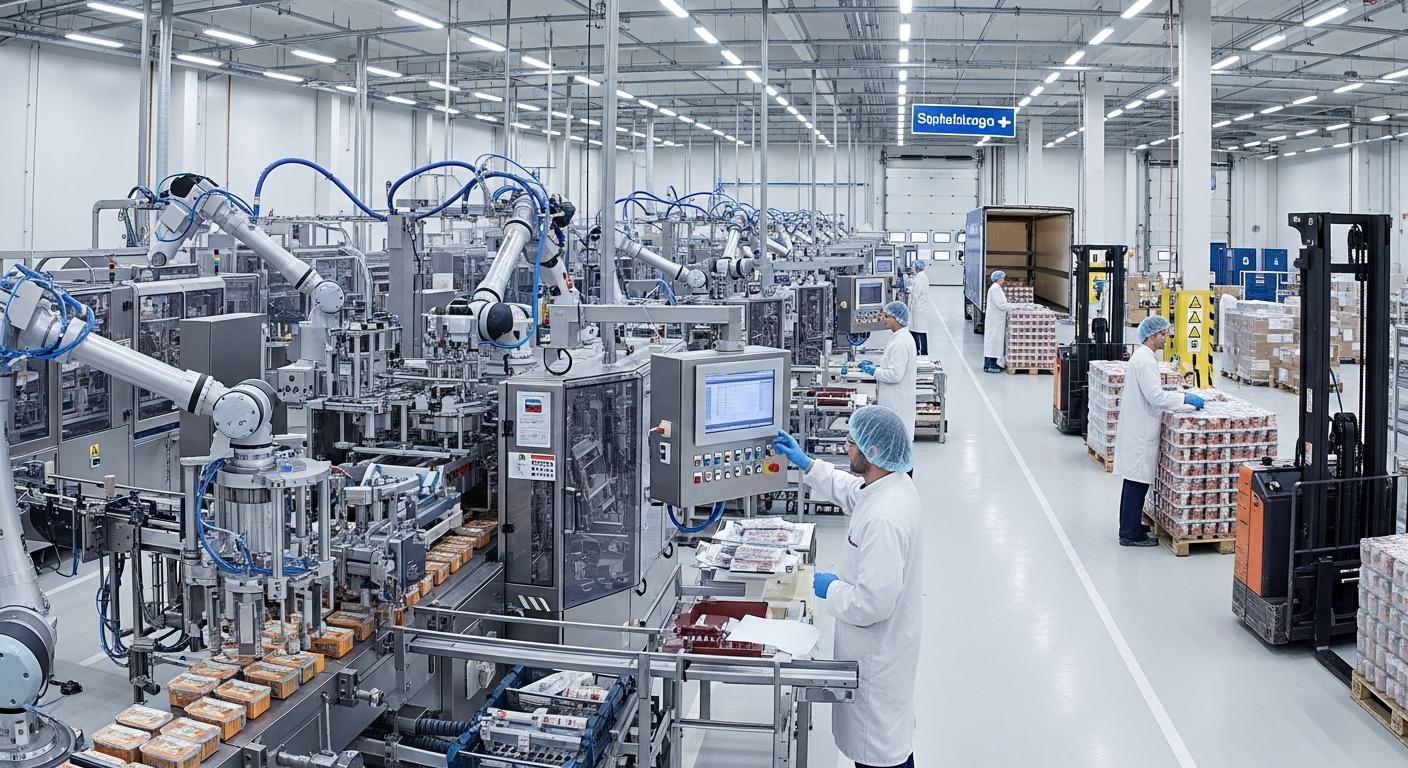

The food packaging industry in Hirakata operates within Japan’s broader manufacturing framework, where precision, quality control, and efficiency remain paramount concerns. This sector encompasses various activities from primary food processing to final packaging operations, serving both domestic consumption and export markets.
Industry Overview: Current Context
Hirakata’s food packaging facilities operate within a highly regulated environment that emphasizes food safety standards and environmental compliance. The industry has adapted to changing consumer preferences, including increased demand for convenient packaging formats and sustainable materials. Local facilities typically handle diverse product categories including processed foods, beverages, and specialty items that require specific packaging technologies.
The sector employs various skill levels, from entry-level positions requiring basic training to specialized roles demanding technical expertise in machinery operation and quality assurance. Manufacturing schedules often accommodate multiple shifts to maximize production capacity and meet delivery requirements.
Food Packaging in Hirakata: What Makes It Distinct?
Hirakata’s food packaging operations benefit from the region’s established supply chain networks and proximity to major urban centers. The city’s industrial zones house facilities that range from small-scale specialty producers to large-scale manufacturing plants serving national distribution channels.
Local operations frequently integrate traditional Japanese manufacturing principles with contemporary automation systems. This approach emphasizes continuous improvement processes, waste reduction, and maintaining consistent product quality standards. Many facilities have implemented advanced tracking systems that monitor products throughout the packaging process.
The geographic advantages include access to raw materials from agricultural regions and efficient transportation links through the Kansai area’s extensive logistics infrastructure.
Production Structure on the Factory Floor
Food packaging facilities in Hirakata typically organize production around specific workflow patterns designed to optimize efficiency and maintain quality standards. The factory floor structure generally includes distinct zones for receiving raw materials, processing, packaging, quality control, and shipping preparation.
Workers operate within clearly defined stations where they perform specific tasks such as machine operation, product inspection, packaging assembly, and materials handling. Modern facilities incorporate automated systems for repetitive tasks while maintaining human oversight for quality assurance and complex operations.
Production schedules are coordinated to minimize downtime and ensure continuous workflow. This includes planned maintenance periods, shift transitions, and coordination with supply chain partners for material deliveries and product shipments.
| Facility Type | Production Focus | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Large-Scale Plants | Mass Production | Automated systems, high volume output, multiple product lines |
| Specialty Facilities | Niche Products | Custom packaging, smaller batches, specialized equipment |
| Contract Packaging | Third-Party Services | Flexible operations, diverse client requirements, adaptable systems |
The industry structure reflects Japan’s emphasis on lean manufacturing principles, where waste reduction and process optimization drive operational decisions. Facilities maintain detailed documentation systems to ensure traceability and compliance with food safety regulations.
Quality control measures are integrated throughout the production process rather than concentrated at final inspection points. This approach helps identify and address potential issues before they affect larger production volumes.
The integration of technology varies among facilities, with larger operations typically employing more sophisticated automation systems while smaller facilities may rely more heavily on manual processes supported by quality control protocols.
Environmental considerations increasingly influence operational decisions, with many facilities implementing energy-efficient systems and exploring sustainable packaging materials. These initiatives often align with corporate sustainability goals and regulatory requirements for environmental impact reduction.
The food packaging industry in Hirakata continues evolving in response to market demands, technological advances, and regulatory changes. This dynamic environment requires facilities to maintain flexibility while preserving the quality standards and operational efficiency that characterize Japanese manufacturing excellence.