Food Packaging Industry in Honcho – Structure and Workflows
The food packaging industry in Honcho is typically presented as a process-driven sector within the food supply chain. Activities follow organized steps related to handling, packing, and quality control. This overview explains in general terms how workflows and working conditions in food packaging environments are usually structured.
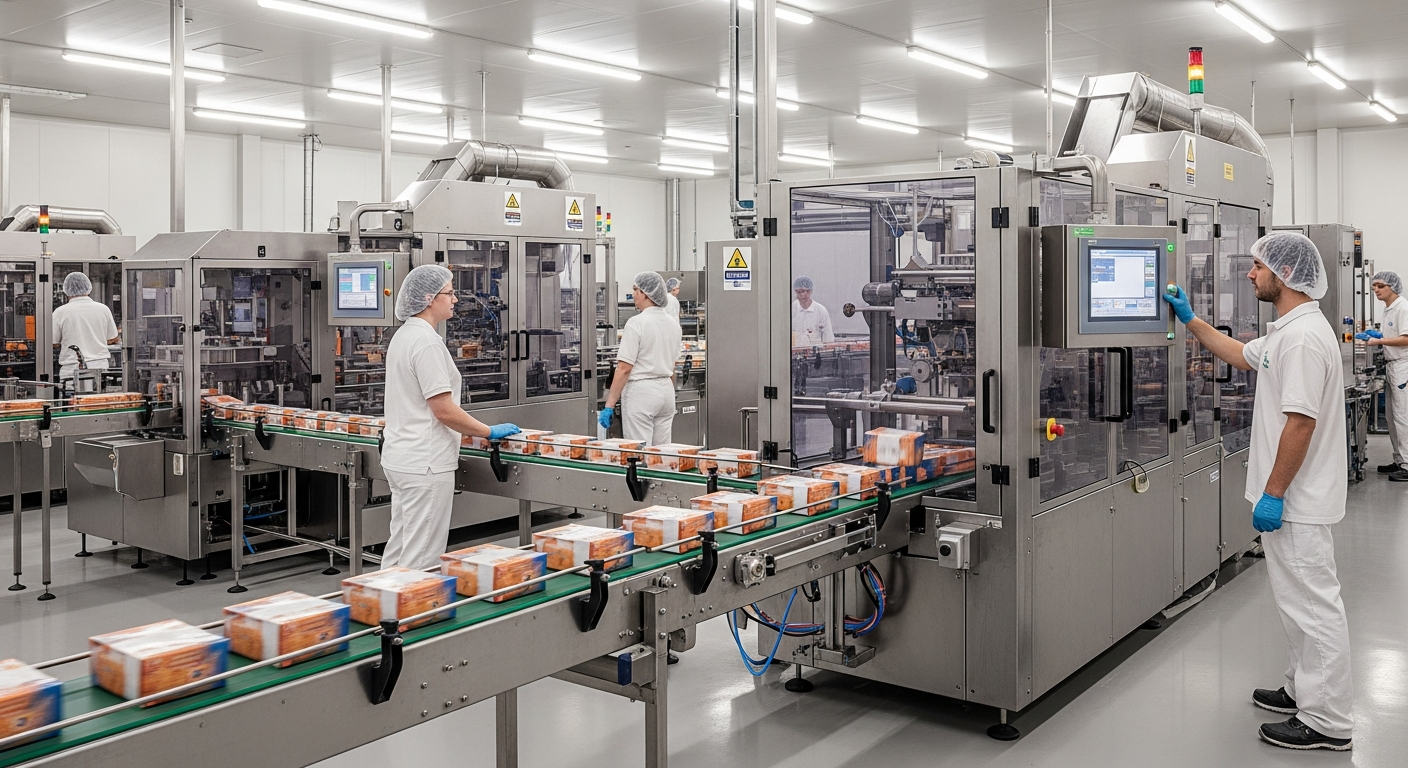

The food packaging industry plays a vital role in ensuring products reach consumers safely and efficiently. In Honcho, this sector has developed distinct characteristics shaped by local manufacturing traditions, technological adoption, and workforce practices. Examining the structure and workflows within this industry reveals how facilities maintain productivity while adhering to strict hygiene and quality standards.
Industry Overview: Current Context
Japan’s food packaging sector has grown steadily over recent decades, driven by demand for convenience foods, export requirements, and domestic consumption patterns. The industry encompasses various processes including primary packaging, secondary packaging, labeling, and quality control. Facilities range from small-scale operations handling specialty products to large automated plants processing high volumes.
Honcho’s position within this landscape reflects broader trends in Japanese manufacturing: emphasis on precision, cleanliness, and continuous improvement. The sector employs a diverse workforce including machine operators, quality inspectors, maintenance technicians, and logistics coordinators. Technological integration has increased, with many facilities adopting automated systems for repetitive tasks while retaining manual oversight for quality assurance.
Regulatory compliance remains central to operations, with facilities adhering to food safety standards established by national authorities. This includes temperature control, contamination prevention, traceability systems, and regular inspections. The industry also responds to environmental concerns through initiatives aimed at reducing packaging waste and improving material recyclability.
Food Packaging in Honcho: What Makes It Distinct?
Several factors distinguish food packaging operations in Honcho from those in other regions. Geographic proximity to both agricultural production areas and urban consumption centers creates logistical advantages, enabling shorter supply chains and fresher product delivery. Local facilities often specialize in packaging specific product categories such as prepared meals, snack foods, or fresh produce, developing expertise in handling particular materials and preservation methods.
The workforce in Honcho typically includes both permanent employees and temporary staff, with training programs designed to ensure all personnel understand hygiene protocols and operational procedures. Many facilities operate multiple shifts to maximize equipment utilization and meet delivery schedules. Communication systems within plants emphasize clarity and efficiency, often using visual management tools to track production progress and identify issues quickly.
Cultural factors also influence workplace dynamics. Japanese manufacturing culture emphasizes teamwork, attention to detail, and respect for established procedures. Workers are encouraged to identify potential improvements through suggestion systems, contributing to incremental efficiency gains. This approach aligns with broader principles of continuous improvement that characterize Japanese industrial practices.
Production Structure on the Factory Floor
The physical layout of food packaging facilities in Honcho follows functional design principles aimed at minimizing contamination risks and optimizing workflow. Typical facilities are organized into distinct zones: receiving areas for incoming materials, preparation sections where products are sorted or processed, packaging lines where items are sealed and labeled, and dispatch areas for completed goods.
Packaging lines vary in complexity depending on product requirements. Simpler operations may involve manual placement of items into containers, while advanced lines incorporate automated feeding systems, sealing machines, metal detectors, weight checkers, and labeling equipment. Operators monitor these systems, performing adjustments and addressing malfunctions as needed. Quality control personnel conduct regular inspections, checking seal integrity, label accuracy, and product condition.
Maintenance routines are scheduled to prevent equipment downtime, with cleaning protocols enforced between production runs to eliminate cross-contamination risks. Facilities maintain detailed records documenting production batches, equipment performance, and quality checks. These records support traceability requirements and provide data for analyzing operational efficiency.
Workflow coordination involves communication between departments to ensure material availability, equipment readiness, and timely completion of orders. Supervisors oversee shift operations, addressing staffing needs and resolving production issues. Logistics teams coordinate with transportation providers to schedule pickups and ensure products reach distribution centers or retail locations according to plan.
Environmental controls maintain appropriate temperature and humidity levels throughout facilities, protecting product quality and worker comfort. Ventilation systems remove heat generated by machinery while air filtration reduces airborne contaminants. Lighting is designed to support accurate inspection and safe movement throughout work areas.
The integration of technology continues to reshape production structures. Facilities increasingly adopt data collection systems that monitor equipment performance in real time, enabling predictive maintenance and reducing unexpected breakdowns. Barcode scanning and RFID technology improve inventory tracking and order accuracy. However, human oversight remains essential, particularly for tasks requiring judgment or handling delicate products.
Training programs prepare workers for their roles, covering safety procedures, equipment operation, hygiene standards, and emergency protocols. New employees typically undergo orientation periods during which they learn facility-specific practices under supervision. Ongoing training addresses equipment updates, regulatory changes, and skill development.
Conclusion
The food packaging industry in Honcho operates within a framework that balances efficiency, quality, and regulatory compliance. Facilities are structured to support smooth workflows while maintaining the cleanliness and precision required for food handling. The sector combines technological advancement with skilled human oversight, reflecting broader characteristics of Japanese manufacturing. Understanding these structures and workflows provides perspective on how the industry meets consumer needs while adapting to evolving market conditions and operational challenges.