Food Packaging Industry in Jurong West – Structure and Workflows
The food packaging industry in Jurong West is typically presented as a process-driven sector within the food supply chain. Activities follow organized steps related to handling, packing, and quality control. This overview explains in general terms how workflows and working conditions in food packaging environments are usually structured.

Singapore’s food packaging sector operates within a highly regulated environment, balancing efficiency with stringent safety and quality standards. Jurong West, as one of the country’s established industrial districts, hosts numerous facilities engaged in various stages of food preparation and packaging. These operations range from primary packaging of fresh produce to secondary packaging of processed goods, serving both domestic consumption and export markets.
Industry Overview: Current Context
The food packaging industry in Singapore has evolved significantly over recent decades, driven by changing consumer demands, technological advancements, and regulatory requirements. Facilities in Jurong West typically handle diverse product categories including ready-to-eat meals, frozen foods, dried goods, and fresh produce. The sector employs a substantial workforce comprising both local residents and foreign workers, with roles spanning manual packaging tasks to quality control and supervisory positions. Automation has gradually been introduced in many facilities, though manual operations remain prevalent, particularly for products requiring careful handling or customized packaging. The industry operates under the oversight of agencies such as the Singapore Food Agency, which enforces standards related to hygiene, labeling, and traceability. Companies must maintain certifications demonstrating compliance with food safety management systems, influencing how workflows are structured and monitored.
Food Packaging in Jurong West: What Makes It Distinct?
Jurong West’s industrial landscape offers specific advantages for food packaging operations. The area benefits from established transportation networks connecting to port facilities and distribution centers, enabling efficient movement of raw materials and finished products. Proximity to other manufacturing and logistics operations creates a supportive ecosystem for supply chain coordination. Many facilities in Jurong West occupy purpose-built industrial spaces designed to accommodate food processing requirements, including temperature-controlled environments, specialized ventilation systems, and segregated zones for different processing stages. The concentration of similar industries in the area has also fostered a localized labor market with relevant skills and experience. Additionally, the presence of supporting service providers—such as packaging material suppliers, equipment maintenance companies, and logistics operators—within the vicinity contributes to operational efficiency. Regulatory compliance infrastructure, including testing laboratories and certification bodies, is readily accessible, facilitating adherence to required standards.
Production Structure on the Factory Floor
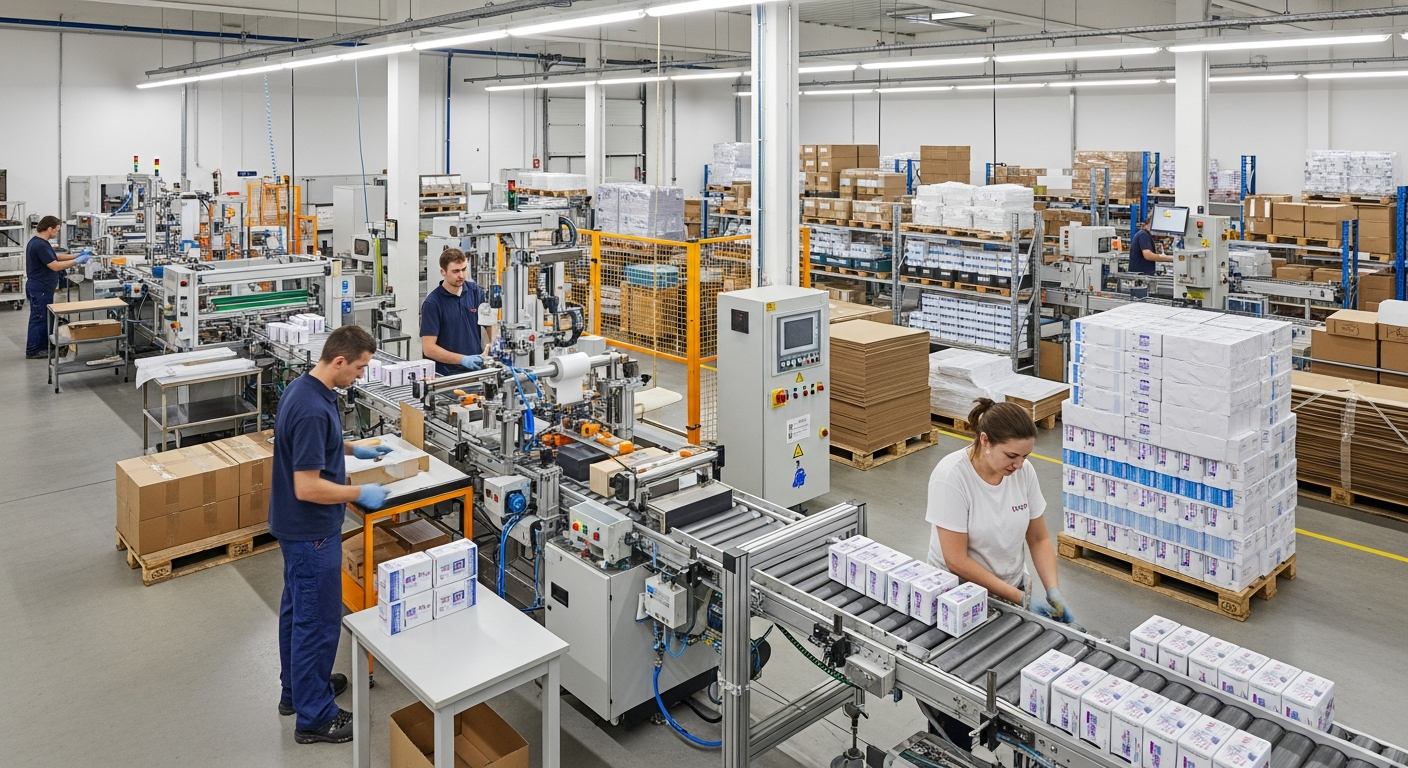
Food packaging facilities in Jurong West typically organize their operations into distinct functional zones, each addressing specific stages of the packaging process. Receiving areas handle incoming raw materials and packaging supplies, where initial quality checks are conducted before materials enter production zones. Preparation sections may involve washing, cutting, portioning, or cooking, depending on the product type. The packaging zone itself often features assembly-line configurations where workers perform tasks such as filling containers, sealing packages, applying labels, and conducting visual inspections. Quality control checkpoints are integrated throughout the workflow, with personnel monitoring for defects, weight accuracy, and seal integrity. Finished products move to staging areas before transfer to cold storage or dispatch zones. Workflow design emphasizes minimizing contamination risks through physical separation of raw and finished product areas, controlled personnel movement, and regular sanitation protocols. Shift structures vary by facility, with many operations running multiple shifts to maximize equipment utilization and meet production targets. Supervisory staff coordinate task assignments, monitor productivity metrics, and address operational issues as they arise.
| Facility Type | Typical Products Handled | Workforce Composition | Key Operational Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fresh Produce Packaging | Vegetables, fruits, salads | Manual workers, quality inspectors | Temperature control, rapid turnover |
| Ready Meal Production | Pre-cooked meals, meal kits | Production line workers, kitchen staff | Cooking facilities, multi-stage assembly |
| Frozen Food Packaging | Frozen vegetables, seafood, processed items | Machine operators, packers | Deep-freeze storage, specialized equipment |
| Dry Goods Packaging | Snacks, dried ingredients, condiments | Packaging operators, labeling staff | Moisture control, extended shelf-life focus |
Workforce requirements in food packaging facilities encompass various skill levels and responsibilities. Entry-level positions typically involve repetitive manual tasks such as product sorting, container filling, or package inspection, with training provided on-site. These roles require attention to detail, adherence to hygiene protocols, and ability to maintain consistent pace throughout shifts. More specialized positions include machine operators who manage automated packaging equipment, quality control technicians who conduct testing and documentation, and maintenance personnel responsible for equipment upkeep. Supervisory and management roles oversee production planning, staff coordination, compliance monitoring, and continuous improvement initiatives. The physical nature of many positions involves standing for extended periods, repetitive motions, and working in temperature-controlled environments. Facilities implement safety measures including protective equipment, ergonomic considerations, and regular breaks to address these demands.
Technological integration continues to reshape food packaging operations in Jurong West. Automated weighing systems, robotic palletizing, and computerized inventory management have been adopted by many facilities to enhance accuracy and efficiency. However, the extent of automation varies considerably based on company size, product characteristics, and capital investment capacity. Smaller operations may rely predominantly on manual processes, while larger facilities increasingly incorporate hybrid systems combining automated and manual elements. Traceability systems have become standard, enabling tracking of products from raw material receipt through final dispatch, supporting both regulatory compliance and recall management capabilities.
The food packaging sector in Jurong West faces ongoing challenges including labor availability, cost pressures, and evolving regulatory requirements. Competition for workers has prompted some facilities to enhance working conditions, provide skills training, and offer performance incentives. Sustainability considerations are increasingly influencing packaging material choices and waste management practices, with companies exploring biodegradable materials and recycling programs. Market demands for product variety and customization add complexity to production planning and inventory management.
Understanding the operational structure and workflows within Jurong West’s food packaging facilities reveals a sector characterized by systematic processes, regulatory compliance, and continuous adaptation to market and technological changes. The industry’s contribution to Singapore’s food security and economic activity underscores its significance within the broader manufacturing landscape, while ongoing developments in automation, sustainability, and workforce management continue to shape its evolution.