Food Packaging Industry in Koriyama – Structure and Workflows
The food packaging industry in Koriyama is typically presented as a process-driven sector within the food supply chain. Activities follow organized steps related to handling, packing, and quality control. This overview explains in general terms how workflows and working conditions in food packaging environments are usually structured.

The food packaging industry in Koriyama operates within Japan’s broader manufacturing ecosystem, where precision and quality control define operational standards. Located in Fukushima Prefecture, Koriyama has developed into a regional center for food processing and packaging, benefiting from its transportation infrastructure and proximity to agricultural regions. The industry encompasses various segments, from fresh produce packaging to processed food containers, each requiring specialized equipment and trained personnel.
Industry Overview: Current Context
Koriyama’s food packaging sector reflects Japan’s commitment to technological advancement and quality assurance. The industry has adapted to changing consumer demands, including increased focus on sustainable packaging materials and extended shelf-life requirements. Local facilities typically employ a combination of automated systems and manual processes, depending on the specific packaging requirements and production volumes. The sector supports both large-scale operations serving national distributors and smaller facilities catering to regional markets.
The industry structure includes primary packaging operations, where products receive their initial protective covering, and secondary packaging processes that prepare items for distribution. Quality control measures remain paramount, with facilities implementing multiple inspection points throughout the packaging workflow. Environmental considerations have become increasingly important, with many operations incorporating recyclable materials and waste reduction protocols.
Food Packaging in Koriyama: What Makes It Distinct?
Koriyama’s food packaging operations distinguish themselves through their integration of traditional Japanese manufacturing principles with contemporary technology. The city’s facilities often specialize in packaging for specific food categories, such as rice products, seafood, or processed foods, allowing for specialized equipment and expertise development. Local operations benefit from established supply chains connecting agricultural producers in the region with packaging facilities.
The workforce in Koriyama’s food packaging sector typically includes both permanent employees and temporary workers, accommodating seasonal fluctuations in production demands. Training programs emphasize food safety protocols, equipment operation, and quality control procedures. Many facilities maintain certification under international food safety standards, enabling them to serve export markets alongside domestic distribution channels.
Technological integration varies across facilities, with larger operations incorporating advanced automation systems for high-volume production lines, while smaller facilities may rely more heavily on manual processes for specialized or custom packaging requirements. This diversity allows the industry to serve a broad range of client needs and market segments.
Production Structure on the Factory Floor
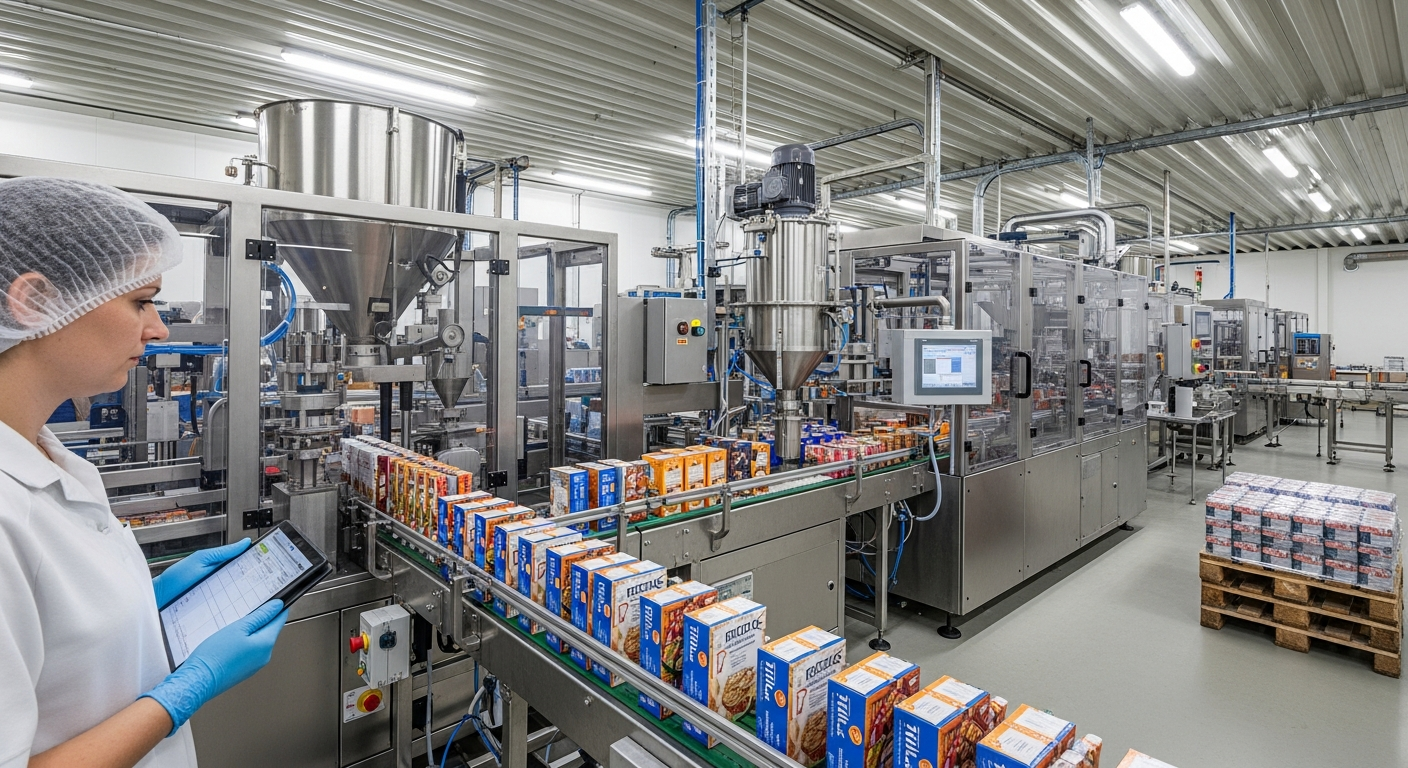
Factory floor operations in Koriyama’s food packaging facilities follow structured workflows designed to maintain product integrity and operational efficiency. Production lines typically begin with incoming material inspection, where packaging materials and food products undergo quality verification before entering the packaging process. Workers are assigned to specific stations along the production line, each with defined responsibilities and quality checkpoints.
The physical layout of packaging facilities prioritizes hygiene and workflow efficiency. Clean rooms and controlled environments are standard for facilities handling sensitive food products, requiring specialized ventilation systems and regular sanitization protocols. Equipment ranges from semi-automated filling machines to fully automated packaging lines capable of processing thousands of units per hour.
Workflow coordination involves multiple departments, including production planning, quality assurance, and logistics coordination. Shift schedules accommodate continuous operation requirements, with many facilities operating multiple shifts to maximize equipment utilization. Communication systems ensure coordination between different production stages and enable rapid response to quality issues or equipment maintenance needs.
Inventory management systems track both incoming materials and finished products, ensuring proper rotation of perishable items and maintaining traceability throughout the packaging process. Documentation requirements include batch records, quality test results, and production logs, supporting both regulatory compliance and customer requirements for product traceability.
The integration of human workers with automated systems requires ongoing training and safety protocols. Workers must understand both manual procedures and automated system operation, enabling them to respond effectively to production variations or equipment issues. Regular maintenance schedules ensure equipment reliability and minimize production disruptions.
Koriyama’s food packaging industry continues to evolve, incorporating new technologies and adapting to changing market demands while maintaining the quality standards that define Japanese manufacturing. The combination of strategic location, skilled workforce, and technological capabilities positions the sector to serve both current market needs and future industry developments.