How to Become a Medical Assistant in the US: Start with Training
Medical assistant roles are becoming more accessible in the United States. Whether you live in a large city or a smaller area, you may not need prior experience to begin. Training programs are available to help newcomers enter the field confidently. With growing healthcare demand, this path offers hands-on work and long-term job potential.
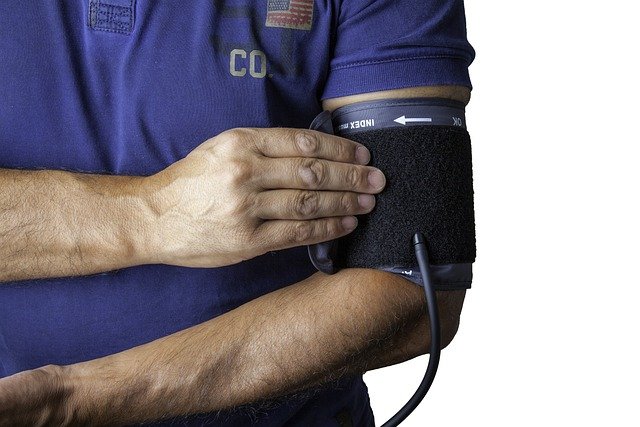
What Does a Medical Assistant Do on a Daily Basis?
Medical assistants perform a wide range of tasks that combine administrative and clinical responsibilities. On a typical day, a medical assistant might:
-
Greet and check in patients
-
Update and file patient medical records
-
Schedule appointments and handle phone calls
-
Measure vital signs, such as blood pressure and temperature
-
Assist physicians during examinations
-
Prepare and administer medications as directed by a physician
-
Perform basic laboratory tests
-
Explain treatment procedures to patients
This diverse set of responsibilities makes the role of a medical assistant both challenging and engaging, requiring a combination of interpersonal skills, attention to detail, and medical knowledge.
How Do Training Programs Help You Enter the Healthcare Field?
Medical assistant training programs are designed to equip aspiring professionals with the knowledge and skills necessary to excel in this field. These programs typically cover:
-
Medical terminology
-
Anatomy and physiology
-
Clinical procedures
-
Administrative tasks
-
Medical law and ethics
-
Electronic health records management
By enrolling in a comprehensive training program, you’ll gain both theoretical knowledge and practical skills through hands-on experience. This combination of classroom learning and clinical practice ensures that you’re well-prepared to handle the diverse responsibilities of a medical assistant upon graduation.
Where Can You Start Your Journey Without Experience?
One of the great advantages of pursuing a career as a medical assistant is that you can often start without prior healthcare experience. Many community colleges, vocational schools, and technical institutes offer medical assistant training programs that cater to individuals with no background in healthcare. These programs are designed to take you from novice to job-ready in a relatively short period, usually ranging from 9 months to 2 years, depending on whether you’re pursuing a certificate, diploma, or associate degree.
What Are the Educational Requirements for Medical Assistants?
While it’s possible to find entry-level medical assistant positions with a high school diploma and on-the-job training, most employers prefer candidates who have completed a formal medical assistant training program. The most common educational paths include:
-
Certificate or Diploma Programs: These typically take 9-12 months to complete and focus on essential skills and knowledge.
-
Associate Degree Programs: These are two-year programs that offer a more comprehensive education, including general education courses.
-
Accredited Programs: Look for programs accredited by organizations like the Commission on Accreditation of Allied Health Education Programs (CAAHEP) or the Accrediting Bureau of Health Education Schools (ABHES).
Completing an accredited program not only enhances your job prospects but also prepares you for certification exams, which can further boost your career opportunities.
How Can You Gain Practical Experience During Training?
Gaining hands-on experience is crucial for aspiring medical assistants. Many training programs incorporate practical components to help students apply their knowledge in real-world settings. Some ways to gain experience include:
-
Clinical rotations: Many programs include externships or clinical rotations in healthcare facilities.
-
Simulation labs: Some schools have on-site labs that mimic real medical environments.
-
Volunteer opportunities: Seek out volunteer positions at local hospitals or clinics.
-
Part-time jobs: Consider entry-level positions in healthcare settings while studying.
-
Job shadowing: Arrange to observe experienced medical assistants in their work environment.
These experiences not only enhance your skills but also provide valuable networking opportunities that could lead to future employment.
What Are the Costs and Options for Medical Assistant Training?
The cost of medical assistant training can vary significantly depending on the type of program and the institution offering it. Here’s a general overview of the costs and options available:
| Program Type | Duration | Average Cost Range | Additional Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Certificate/Diploma | 9-12 months | $1,200 - $4,000 | Faster entry into workforce |
| Associate Degree | 2 years | $10,000 - $30,000 | More comprehensive education |
| Online Programs | Varies | $1,000 - $15,000 | Flexible scheduling options |
| Community College | 1-2 years | $2,500 - $10,000 | Often more affordable |
| Private Career Schools | 9-24 months | $6,000 - $30,000 | May offer job placement assistance |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
When considering the cost of training, it’s important to factor in additional expenses such as textbooks, supplies, and certification exam fees. Many schools offer financial aid options, including grants, scholarships, and payment plans, to help make the training more accessible.
In conclusion, becoming a medical assistant in the US starts with choosing the right training program that fits your goals and circumstances. With the growing demand for healthcare professionals, investing in medical assistant training can open doors to a rewarding career with ample opportunities for growth and specialization. By carefully considering your options and committing to a comprehensive education, you’ll be well on your way to joining this vital profession in the healthcare industry.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.