Portable laser welding machines improve accuracy and efficiency in Spain
In Spain, portable laser welding machines are transforming the welding landscape by improving accuracy, saving time, and reducing costs. This technology is particularly beneficial in various sectors, such as manufacturing and construction. A closer look at the different models, pricing structures, and practical applications reveals their growing importance in welding manufacturing processes. Furthermore, effective welding training for workers is essential to maximizing the potential of these advanced machines.
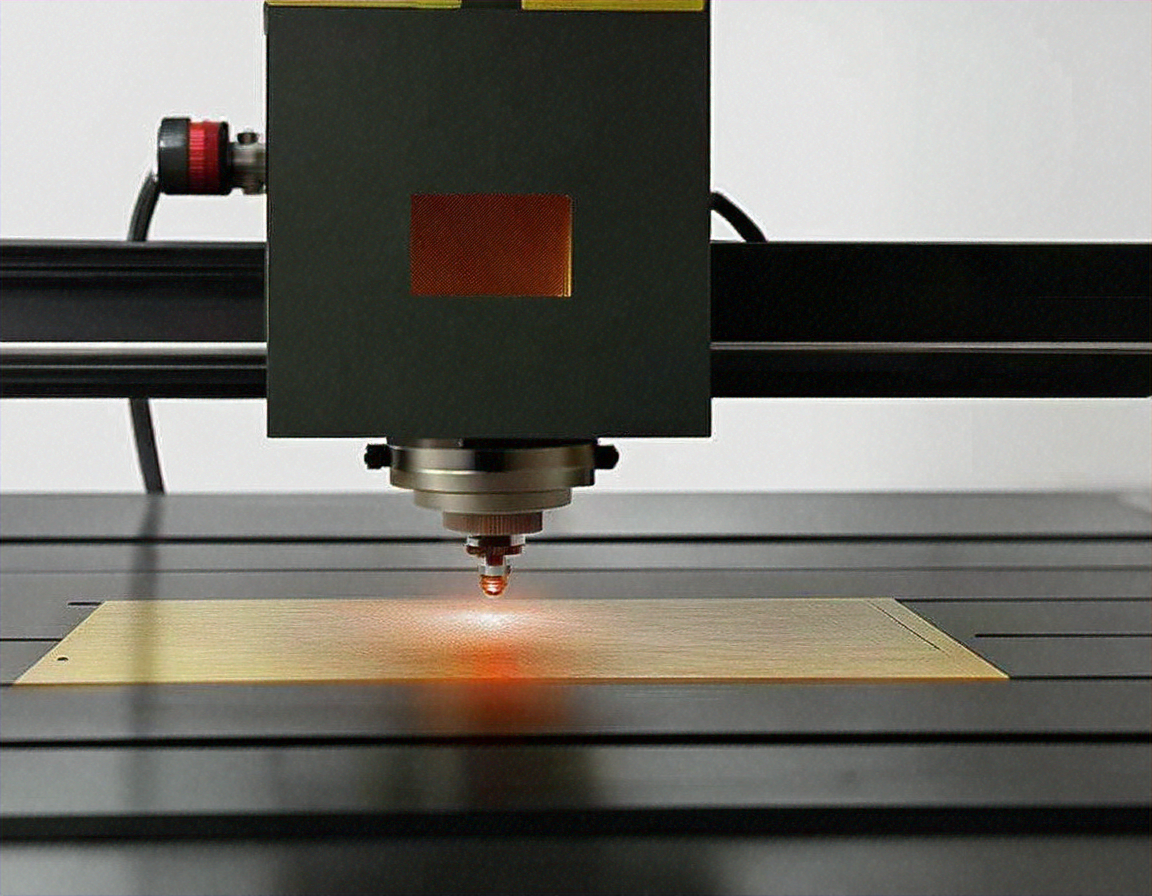
Portable laser welding technology represents a significant advancement in metal joining processes, offering Spanish industries new possibilities for precision work and operational flexibility. These systems deliver focused energy beams that create strong, clean welds while minimizing heat-affected zones and material distortion. Understanding how these machines function and their practical applications helps businesses make informed decisions about adopting this technology.
What are portable laser welding machines and what advantages do they offer?
Portable laser welding machines are handheld or mobile welding systems that use concentrated laser beams to join metal components. Unlike traditional welding equipment that requires stationary setups, these devices can be transported to different work locations, making them ideal for on-site repairs and fabrication tasks. The laser beam generates intense heat at a precise point, melting the metal surfaces and creating a fusion bond as the material cools.
These machines offer several distinct advantages over conventional welding methods. First, they provide exceptional precision, allowing operators to work on intricate designs and small components without damaging surrounding areas. The focused heat input reduces warping and distortion, which is particularly valuable when working with thin materials or heat-sensitive assemblies. Second, portable laser welding produces cleaner welds with minimal spatter and reduced post-weld finishing requirements, saving time and labor costs.
Another significant benefit is the speed of operation. Laser welding completes joints faster than traditional methods, increasing productivity in manufacturing environments. The technology also enables welding of dissimilar metals that would be challenging with conventional techniques. Additionally, the portability aspect eliminates the need to move large workpieces to stationary welding stations, reducing handling time and potential damage to finished products.
The reduced heat-affected zone minimizes the risk of metallurgical changes in the base material, preserving the mechanical properties of the components being joined. This characteristic makes laser welding particularly suitable for high-strength alloys and precision applications where material integrity is critical.
In which industrial sectors is laser welding used?
Laser welding technology has found applications across numerous industrial sectors in Spain, each benefiting from the precision and efficiency these systems provide. The automotive industry represents one of the largest users of laser welding, employing the technology for body panel assembly, exhaust system fabrication, and battery pack construction for electric vehicles. The ability to create strong, lightweight joints without adding excessive material makes laser welding ideal for modern vehicle manufacturing.
The aerospace sector relies heavily on laser welding for fabricating critical components where strength-to-weight ratios are paramount. Aircraft structural elements, engine components, and fuel system parts often require the precision and quality that laser welding delivers. The technology allows manufacturers to meet stringent safety standards while maintaining production efficiency.
Medical device manufacturing utilizes portable laser welding for creating surgical instruments, implantable devices, and diagnostic equipment. The clean, precise welds are essential for products that must meet strict hygiene and biocompatibility requirements. Jewelry and watchmaking industries also benefit from laser welding, as the focused energy allows artisans to repair delicate pieces and create intricate designs without damaging gemstones or sensitive mechanisms.
The electronics sector employs laser welding for assembling battery packs, connecting thin-walled housings, and creating hermetic seals for sensitive components. Shipbuilding and marine repair operations use portable laser welding systems for on-site maintenance and fabrication tasks where transporting large structures to workshop facilities would be impractical. Metal fabrication shops, construction companies, and maintenance service providers across Spain increasingly adopt this technology to enhance their service capabilities and competitive positioning.
Why is laser welding training essential?
Proper training for laser welding operators is not merely recommended but essential for safe, effective use of these sophisticated systems. Unlike traditional welding methods that many technicians learn through apprenticeships, laser welding requires specialized knowledge of laser physics, safety protocols, and equipment operation. Without adequate training, operators risk personal injury, equipment damage, and production of substandard welds that could compromise structural integrity.
Laser systems generate intense light and heat that can cause serious eye injuries and skin burns if proper safety measures are not followed. Training programs teach operators about laser classifications, protective equipment requirements, and safe working distances. Understanding these safety principles protects not only the operator but also nearby workers who might be exposed to reflected laser beams or welding fumes.
Technical training covers parameter selection for different materials and joint configurations. Operators must learn how laser power, beam focus, welding speed, and shielding gas selection affect weld quality. Each material combination requires specific settings, and improper parameters can result in weak joints, excessive porosity, or incomplete fusion. Training programs provide hands-on experience with various materials and thicknesses, building the practical skills necessary for consistent results.
Maintenance knowledge is another critical component of laser welding training. These machines contain sophisticated optical systems, cooling components, and control electronics that require regular inspection and servicing. Trained operators can identify potential problems before they cause equipment failures, reducing downtime and repair costs. They also learn troubleshooting techniques for addressing common issues that arise during production.
Quality control training ensures operators can inspect their work and recognize defects that might compromise weld integrity. Understanding metallurgical principles helps technicians predict how different materials will respond to laser welding and adjust their approach accordingly. As laser welding technology continues to evolve, ongoing training keeps operators current with new capabilities and best practices, maximizing the return on investment in these advanced systems.
Portable laser welding machines represent a significant technological advancement for Spanish industries seeking to improve manufacturing precision and operational efficiency. The combination of portability, precision, and speed makes these systems valuable across diverse sectors, from automotive production to jewelry repair. However, realizing the full potential of laser welding technology requires commitment to proper operator training and adherence to safety protocols. As more businesses recognize these benefits, laser welding is likely to become increasingly common in workshops and production facilities throughout Spain.




