Start Your Plumbing Career with Training Internship in Switzerland
Switzerland's robust construction industry and commitment to skilled trades education create an ideal environment for aspiring plumbers to develop their careers. The country's apprenticeship system, combined with modern training facilities and high industry standards, provides comprehensive pathways for those interested in plumbing careers. While specific program availability varies by region and institution, understanding the general landscape of plumbing education can help prospective students make informed decisions about their career development.

What Training Opportunities Exist in Swiss Plumbing Education?
When you explore comprehensive plumber training opportunities in Switzerland, you’ll discover that the country follows a dual education system combining theoretical knowledge with hands-on experience. Swiss plumbing training typically spans three to four years, integrating classroom instruction with practical workplace learning. Students learn essential skills including pipe installation, water system maintenance, heating system basics, and modern plumbing technologies.
Training programs generally cover sanitary installations, water supply systems, drainage solutions, and increasingly important sustainable plumbing practices. The curriculum often includes safety protocols, blueprint reading, and customer service skills essential for professional success. Many programs also incorporate digital tools and smart home technologies that are becoming standard in modern plumbing installations.
How Do Funded Training Programs Support Career Development?
Various funding mechanisms may support plumbing education in Switzerland, though availability depends on specific circumstances and regional programs. When fully-funded internship programs for aspiring plumbers are available, they typically combine employer sponsorship with government support for vocational education. These arrangements often provide students with practical income while learning, making career transitions more financially feasible.
Funding sources may include cantonal education departments, industry associations, and individual employers seeking skilled workers. Some programs offer tool allowances, transportation support, or housing assistance for students relocating for training opportunities. However, funding availability and eligibility requirements vary significantly based on location, program type, and individual circumstances.
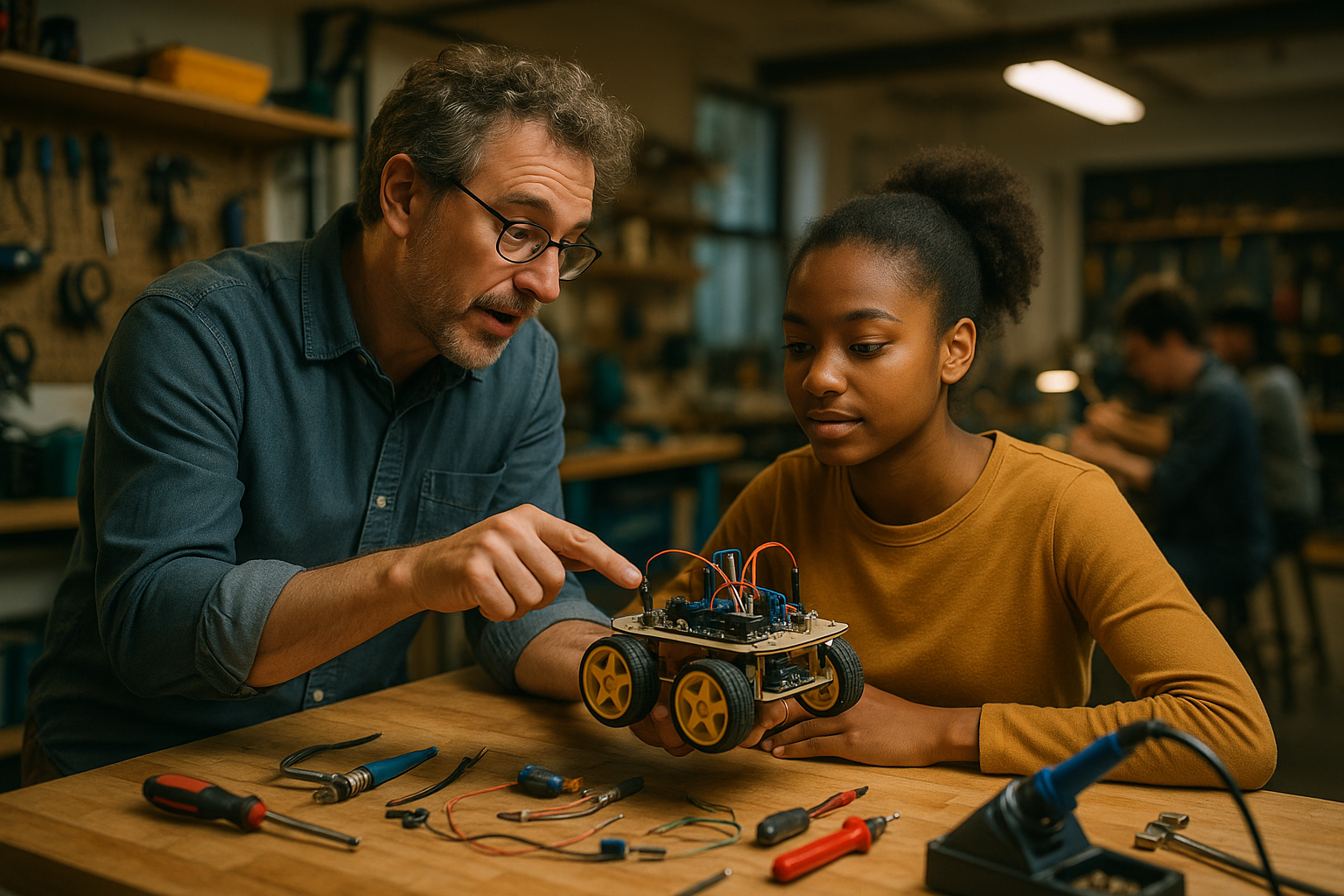
What Practical Skills Development Can Students Expect?
Students gain practical skills in plumbing with expert guidance and support through structured learning environments that emphasize real-world application. Training typically includes hands-on workshops where students practice pipe cutting, joining techniques, fixture installation, and system testing procedures. Experienced master plumbers often serve as mentors, providing personalized instruction and career guidance.
Practical training components usually cover emergency repair procedures, preventive maintenance techniques, and troubleshooting methodologies. Students learn to work with various materials including copper, PVC, steel, and modern composite materials. Many programs also include specialized training in energy-efficient systems, heat pumps, and renewable energy integration reflecting Switzerland’s environmental priorities.
How Does Switzerland’s Apprenticeship System Work?
Switzerland’s renowned apprenticeship system typically combines workplace learning with formal education, creating well-rounded professionals. Plumbing apprentices usually spend three to four days per week with employer partners and one to two days in vocational schools. This structure ensures students develop both technical skills and theoretical understanding necessary for professional competence.
The system emphasizes progressive skill development, with apprentices taking on increasingly complex tasks as they advance. Regular assessments and practical examinations ensure quality standards are maintained throughout the training process. Many apprenticeship programs culminate in nationally recognized certifications that provide strong foundations for career advancement.
What Career Prospects Exist After Training Completion?
Switzerland’s construction industry offers various career paths for qualified plumbers, from residential service work to commercial installation projects. Skilled plumbers may advance to supervisory roles, start independent businesses, or specialize in areas like sustainable energy systems or smart building technologies. The country’s high construction standards and ongoing infrastructure development create steady demand for qualified professionals.
Career advancement often includes opportunities for additional certifications in specialized areas such as solar heating systems, geothermal installations, or building automation. Many plumbers eventually become self-employed, taking advantage of Switzerland’s favorable business environment and strong demand for quality craftsmanship.
| Training Provider Type | Program Duration | Typical Features |
|---|---|---|
| Vocational Schools | 3-4 years | Classroom instruction, basic workshops, theory focus |
| Employer Apprenticeships | 3-4 years | Workplace learning, mentorship, practical emphasis |
| Technical Colleges | 2-3 years | Advanced techniques, specialized systems, higher certification |
Training availability, duration, and features vary by institution and region. Prospective students should research current offerings through official educational channels.
What Should Prospective Students Consider?
Individuals interested in plumbing careers should research current program availability through official educational channels and cantonal vocational guidance offices. Program requirements, application processes, and start dates vary significantly between regions and institutions. Language proficiency in local languages (German, French, or Italian) is typically essential for successful participation in training programs.
Physical fitness, problem-solving abilities, and attention to detail are important personal attributes for plumbing careers. Prospective students should also consider the demanding nature of the work, which often involves working in confined spaces, lifting heavy materials, and responding to emergency situations.
Switzerland’s plumbing training landscape offers multiple pathways for career development, though specific opportunities require individual research and application through appropriate educational and industry channels. The combination of theoretical education, practical experience, and mentorship available through Swiss training systems provides strong foundations for successful plumbing careers, while the country’s commitment to skilled trades ensures ongoing opportunities for qualified professionals.
This article provides general information about plumbing training pathways and should not be interpreted as indicating specific available positions or active recruitment. Prospective students should research current program availability and requirements through official educational institutions and vocational guidance services.