The Silent Symphony: Decoding Canine Body Language
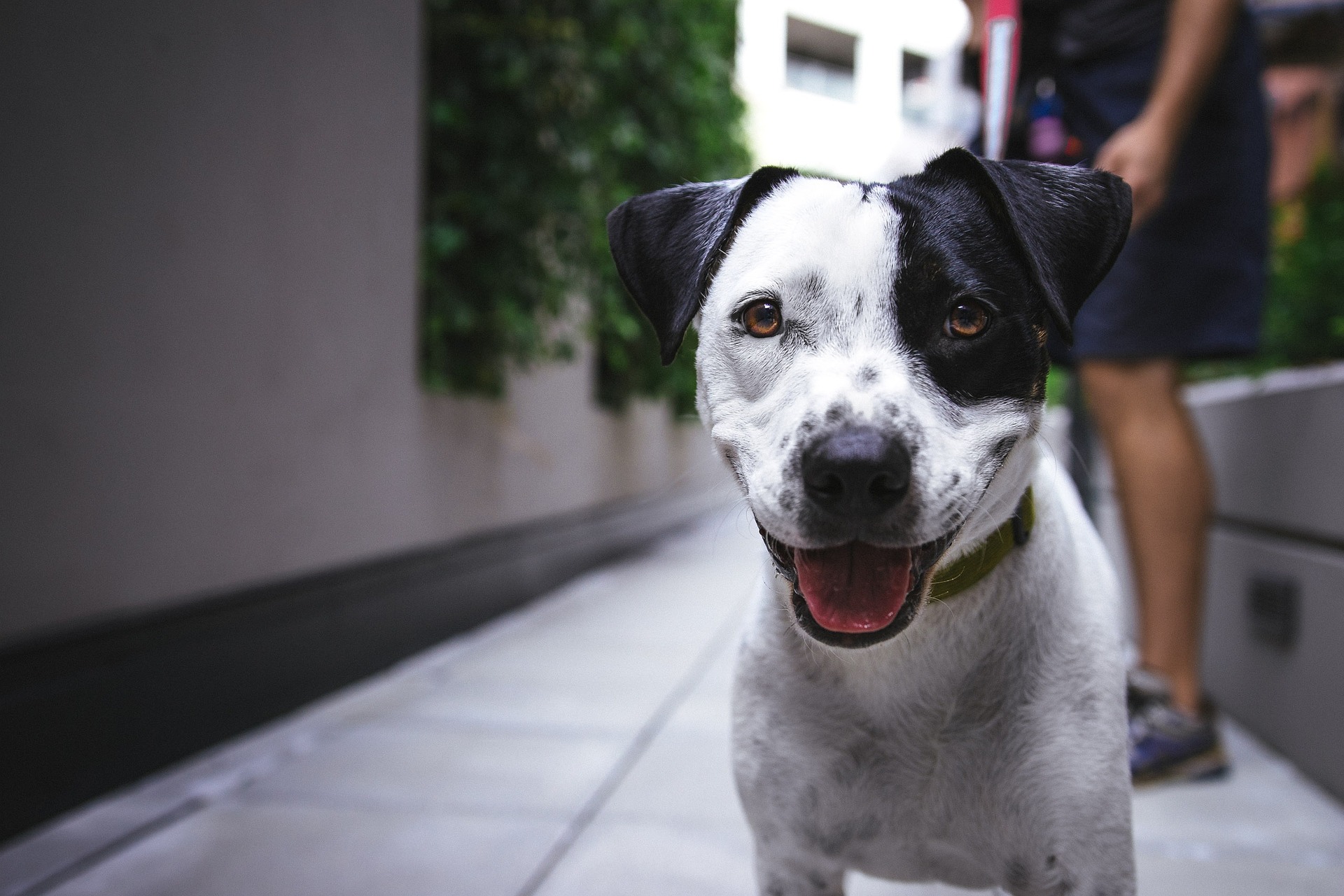
Have you ever wondered what your dog is trying to tell you when they wag their tail or tilt their head? Dogs communicate through a complex language of body movements, facial expressions, and vocalizations. In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of canine body language, exploring the hidden meanings behind their behaviors and providing you with the tools to better understand your furry companion.
Have you ever wondered what your dog is trying to tell you when they wag their tail or tilt their head? Dogs communicate through a complex language of body movements, facial expressions, and vocalizations. In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of canine body language, exploring the hidden meanings behind their behaviors and providing you with the tools to better understand your furry companion.
1. The Eyes Have It: Understanding Canine Gaze
- Direct eye contact: A direct, unblinking gaze can indicate dominance or aggression in some dogs. However, in others, it may simply mean they are focused and engaged.
- Blinking: Rapid blinking or squinting can be a sign of discomfort or submission.
- Dilated pupils: Dilated pupils may indicate excitement, fear, or aggression.
- Staring: Prolonged staring can be a sign of dominance or aggression, but it can also be a sign of affection or curiosity.
2. The Power of Posture: Interpreting Canine Body Language
- Tail position: A high, stiff tail indicates confidence and alertness, while a low, tucked tail can signal fear or submission.
- Ear position: Forward-facing ears indicate interest or alertness, while flattened ears can signal fear or submission.
- Body language: A relaxed dog will have a loose, sagging body, while a tense or anxious dog will have a stiff, rigid body.
- Play bow: A play bow, where a dog lowers its front end and raises its hind end, is a sign of playfulness and friendliness.
3. The Language of Movement: Reading Canine Body Movements
- Tail wagging: A tail wag can indicate a variety of emotions, from happiness and excitement to fear and aggression. The direction and speed of the wag can provide additional clues.
- Lip licking: Lip licking can be a sign of stress, anxiety, or discomfort, but it can also be a sign of submission or appeasement.
- Shaking off: Shaking off can be a sign of excitement or nervousness, but it can also be a way for a dog to relieve tension or discomfort.
- Barking: Barking can indicate a variety of emotions, from excitement and playfulness to fear and aggression. The pitch, volume, and duration of the bark can provide additional clues.
4. The Art of Interpretation: Putting It All Together
- Context is key: Understanding canine body language requires taking into account the context of the situation, as well as the individual dog’s personality and history.
- Practice makes perfect: The more you observe and interact with dogs, the better you will become at interpreting their body language.
- Seek professional help: If you are unsure about a dog’s body language or behavior, seek the advice of a professional dog trainer or behaviorist.
5. The Future of Canine Communication: Advances in Research
- Recent studies have shown that dogs can understand human pointing gestures, and that they can even follow human eye gaze.
- Researchers are also exploring the use of technology, such as wearable devices and artificial intelligence, to better understand and interpret canine body language.
- As our understanding of canine communication continues to evolve, we can look forward to even more effective and compassionate ways of interacting with our furry friends.
By understanding canine body language, we can build stronger, more meaningful relationships with our dogs. Whether you’re a seasoned dog owner or a newcomer to the world of canine companionship, this article will provide you with the knowledge and tools you need to decode your dog’s silent symphony.