Waste Management Industry in Amagasaki – General Informational Overview
If you live in Amagasaki, you may be interested in learning how the waste management industry is typically organized across the country. This sector supports environmental protection and urban infrastructure through structured collection systems, sorting facilities, recycling processes, and regulatory compliance frameworks. Learn more about how waste management workflows are usually structured. Discover more inside.
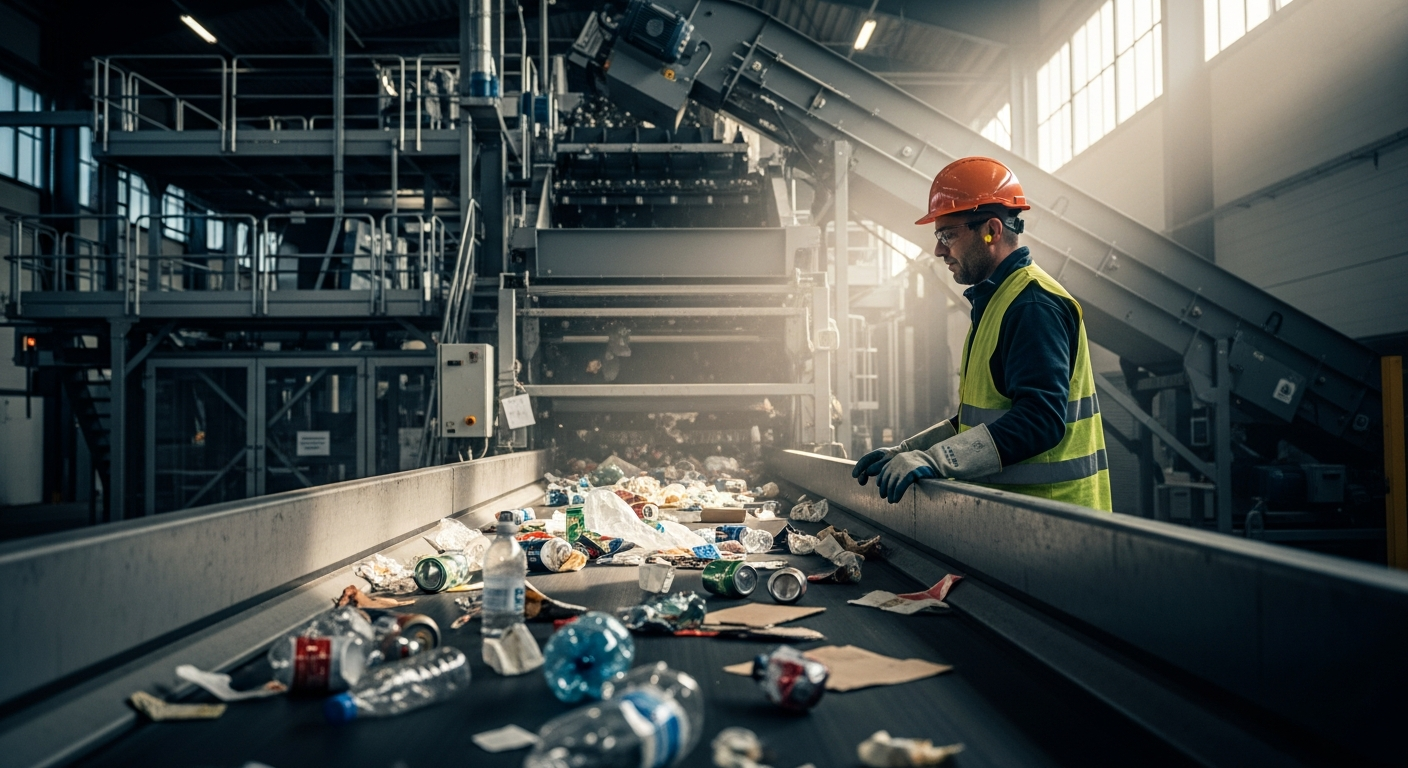

How Do Waste Collection and Sorting Processes Work in Amagasaki?
Waste collection and sorting in Amagasaki begin with a highly structured system that relies significantly on resident participation. Households and businesses are provided with detailed guidelines on separating waste into various categories, such as burnable waste, non-burnable waste, plastics, glass bottles, cans, paper, and large-sized refuse. Specific collection days are designated for each waste type, and residents are expected to dispose of their sorted waste in designated bags or containers at specific collection points. This source separation is a cornerstone of effective waste management, significantly reducing the effort required at later stages and improving the quality of materials sent for recycling or treatment. Commercial establishments also adhere to stringent sorting rules, often utilizing private collection services that align with local regulations.
What Happens at Recycling and Treatment Facility Operations?
Once collected, the sorted waste in Amagasaki embarks on different paths depending on its classification. Recyclable materials, such as plastics, glass, and paper, are transported to dedicated recycling facilities where they undergo further sorting, cleaning, and processing to prepare them for reuse in manufacturing new products. Burnable waste is typically directed to incineration plants. These modern facilities are equipped with advanced technologies to burn waste efficiently while minimizing emissions, often generating electricity in the process, contributing to the local energy supply. Non-burnable waste and residues from incineration are carefully managed and disposed of in designated landfills, adhering to strict environmental standards to prevent soil and water contamination. Organic waste may also be processed separately for composting or other forms of resource recovery, depending on local programs.
How Are Environmental Compliance and Safety Standards Maintained?
Maintaining environmental compliance and safety standards is paramount within Amagasaki’s waste management sector. Operations across collection, sorting, recycling, and treatment facilities are governed by national and local environmental laws and regulations. These regulations dictate emission limits for incineration plants, proper landfill management practices, and strict handling protocols for hazardous waste. Regular inspections and monitoring are conducted by regulatory bodies to ensure that facilities adhere to these standards, protecting both the environment and public health. Furthermore, worker safety is a critical consideration, with comprehensive training programs, personal protective equipment, and operational protocols in place to mitigate risks associated with waste handling, machinery operation, and exposure to various materials. Continuous improvement initiatives are often implemented to enhance both environmental performance and safety records across the industry.
Amagasaki’s waste management system represents a coordinated effort involving residents, businesses, and municipal services. The emphasis on source separation, advanced facility operations, and rigorous adherence to environmental and safety standards underpins a system designed for sustainability. This integrated approach not only manages the city’s waste effectively but also contributes to resource conservation and a cleaner urban environment. The continuous evolution of technologies and practices further strengthens the framework for future waste management challenges.