Waste Management Industry in Hamamatsu – General Informational Overview
If you live in Hamamatsu, you may be interested in learning how the waste management industry is typically organized across the country. This sector supports environmental protection and urban infrastructure through structured collection systems, sorting facilities, recycling processes, and regulatory compliance frameworks. Learn more about how waste management workflows are usually structured. Discover more inside.
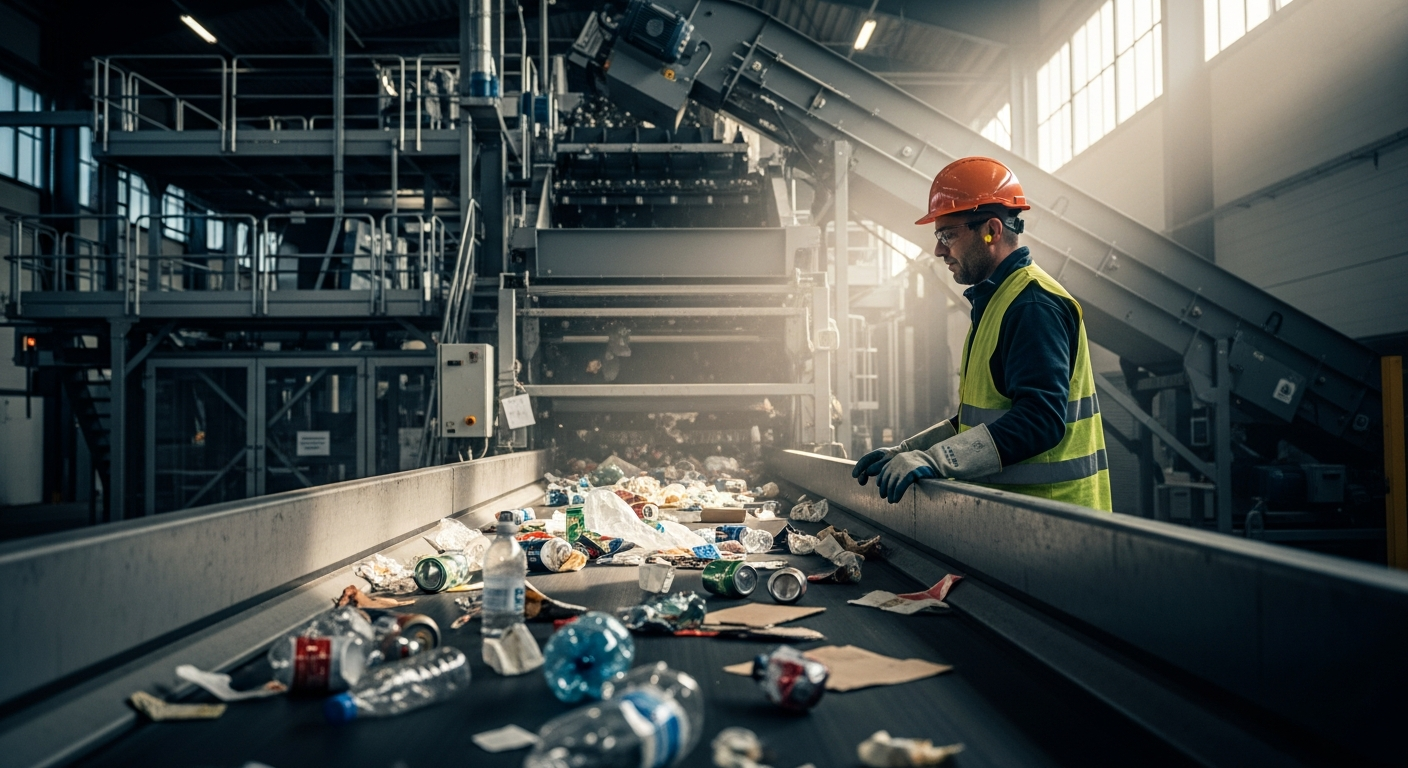

The waste management sector in Hamamatsu represents a critical infrastructure component that supports both residential communities and the city’s significant industrial base, including major automotive and electronics manufacturing facilities. This system operates through multiple interconnected processes designed to maximize resource recovery while minimizing environmental impact.
How Do Waste Collection and Sorting Processes Work in Hamamatsu
Hamamatsu implements a detailed waste separation system that requires residents and businesses to sort materials into specific categories before collection. The city operates on a scheduled collection system where different types of waste are collected on designated days throughout the week. Burnable waste, including food scraps and paper products, is typically collected twice weekly, while recyclable materials such as plastic containers, glass bottles, and metal cans follow separate schedules.
Collection vehicles follow predetermined routes through residential neighborhoods and commercial districts, with specialized equipment designed to handle different waste types. The sorting process begins at the household level, where residents must separate materials according to city guidelines, and continues at collection points where additional sorting may occur. This systematic approach ensures that materials reach appropriate processing facilities and reduces contamination between waste streams.
What Happens at Recycling and Treatment Facility Operations
The city operates several specialized facilities that process different waste categories collected throughout Hamamatsu. The main incineration plant handles burnable waste using advanced combustion technology that generates electricity while minimizing emissions. This facility processes thousands of tons of waste monthly and contributes to the city’s energy grid through waste-to-energy conversion.
Recyclable materials are processed at dedicated sorting facilities where automated systems and manual sorting separate materials by type and quality. Glass bottles are sorted by color, plastic containers are categorized by resin type, and metal items are separated for different recycling processes. These facilities employ various technologies including optical sorting systems, magnetic separators, and density separation equipment to achieve high-quality recycled materials.
Organic waste processing occurs at composting facilities that convert food waste and yard trimmings into usable compost products. These operations use controlled decomposition processes that manage temperature, moisture, and aeration to produce high-quality soil amendments used in local agriculture and landscaping projects.
How Are Environmental Compliance and Safety Standards Maintained
Hamamatsu’s waste management operations must comply with strict Japanese environmental regulations that govern air emissions, water quality, and soil contamination. Regular monitoring systems track emissions from incineration facilities, ensuring compliance with national air quality standards. Water treatment systems at processing facilities prevent contaminated runoff from entering local waterways, while soil testing around facilities monitors for potential contamination.
Safety protocols protect workers throughout the waste management system, from collection crews to facility operators. Personal protective equipment requirements, vehicle safety systems, and facility safety procedures are regularly updated based on industry best practices and regulatory requirements. Training programs ensure that personnel understand proper handling procedures for different waste types, including hazardous materials that require special processing.
Quality control measures include regular inspections of collection vehicles, facility equipment maintenance schedules, and monitoring of processed materials to ensure they meet standards for recycling or disposal. Environmental impact assessments are conducted periodically to evaluate the effectiveness of waste reduction initiatives and identify areas for system improvements.
The integration of these operational components creates a comprehensive waste management system that serves Hamamatsu’s diverse needs while maintaining high environmental and safety standards. This approach reflects broader Japanese principles of resource conservation and environmental stewardship that influence waste management practices throughout the country. The system’s effectiveness depends on cooperation between municipal authorities, private contractors, and community members who participate in proper waste separation and disposal practices.
Understanding these operational aspects provides valuable context for anyone interested in how modern urban waste management systems function in Japan’s industrial cities. The Hamamatsu model demonstrates how systematic approaches to waste collection, processing, and environmental compliance can effectively manage the complex waste streams generated by both residential and industrial activities.